Figure 3.
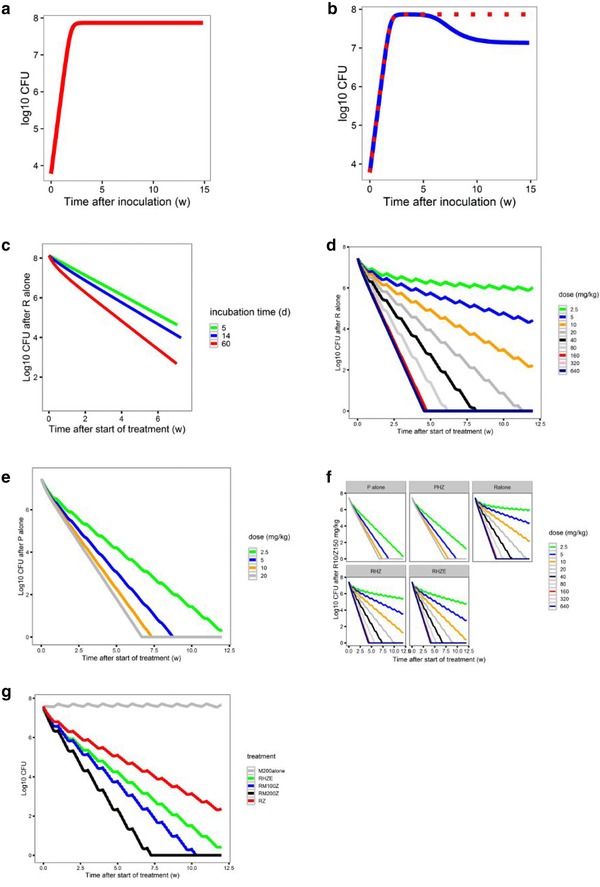
Components of the pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) model. (a) Baseline model of bacterial growth in mice without immune function (red). (b) Bacterial growth in untreated mice is dependent on the immune competency (immune‐competent BALB/c mice, blue; immune‐deficient nude mice, red). (c) The additive effect of immune function on the killing effect of rifampin (R) alone is smaller in acute infection models (5‐day [green] or 14‐day [blue] incubation period prior to treatment onset [time 0]) compared with a chronic infection model (61‐day incubation period (red). Simulation of the concentration‐colony forming unit (CFU) count relationship of (d) rifampin alone, or (e) rifapentine (P) alone, at different dose levels tested in the mouse model. (f) The effect of combining R or P with isoniazid (H) 25 mg/kg and pyrazinamide (Z) 150 mg/kg ± E 100 mg/kg in immune‐competent mice. (g) The estimated effect of moxifloxacin in combination with R10 mg/kg and Z 150 mg/kg and predicted effect of moxifloxacin alone*. E, ethambutol; M, moxifloxacin. *Moxifloxacin alone simulations alone effect was based on the difference in effect between rifampin/ pyrazinamide and rifampin/moxifloxacin/pyrazinamide.
