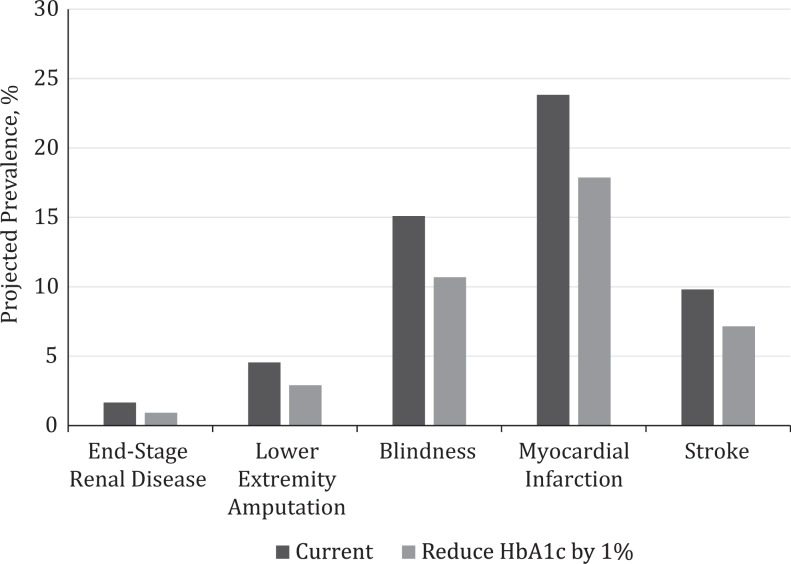
Figure 2.
Prevalence projections for diabetic complications occurring before and after reducing hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) by 1% among adults with prediabetes and diabetes in San Antonio, Texas, during a 20-year period (2015-2034). In the “current” scenario (before reducing HbA1c by 1 percentage point), the simulated population had the same HbA1c distribution that was estimated from the Diabetes HbA1c Registry in San Antonio, 2011. In the “reduce HbA1c by 1 percentage point” scenario (after reducing the HbA1c by 1 percentage point), each person in the simulated population had a 1-percentage-point reduction in HbA1c at the beginning of the simulation.