Figure 1. Hyperosmotic stress stimulates autophagy.
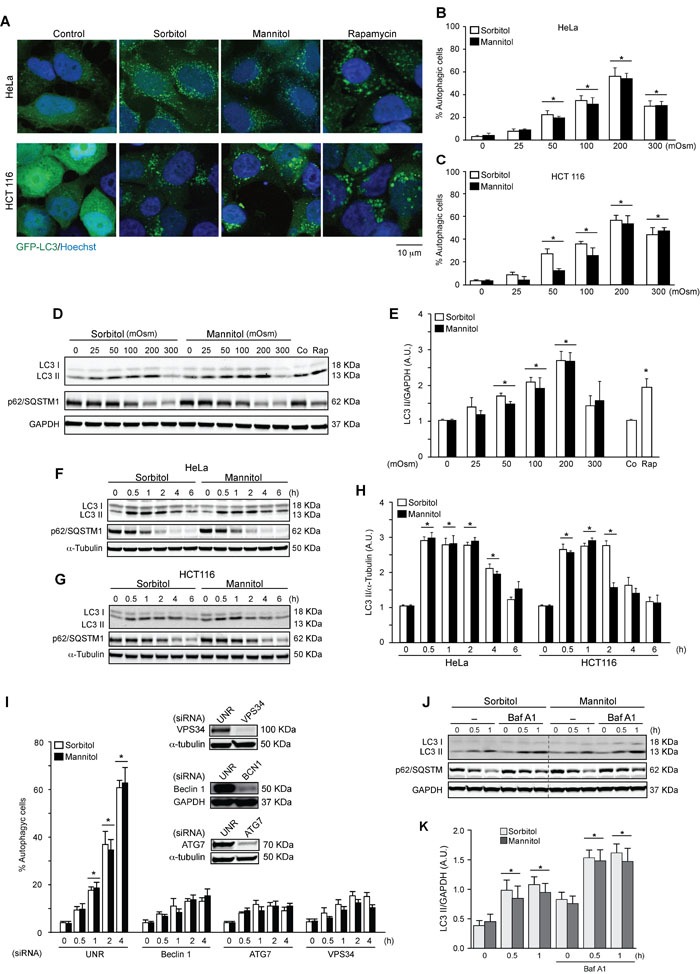
HeLa and HCT 116 cells were transduced with an adenovirus coding for GFP-LC3 (Ad GFP-LC3) for 24 h. Cultures were then exposed to different concentrations (25-300 mOsm) of sorbitol or mannitol for 2 h. Subsequently, autophagy was evaluated by fluorescent microscopy. 1 μM of rapamycin was used as a positive control to induce autophagy. Nuclei were dyed with 10 ng/mL of DAPI. Representative pictures are shown in A.. The percentage of cells with GFP-LC3 puncta (autophagic cells) in HeLa and HCT116 are shown in B. and C., respectively (mean ± SEM, n = 3, *p < 0.05 vs. 0 mOsm). LC3 I-to-LC3 II conversion and p62/SQSTM1 depletion were assessed by Western blot analysis in HeLa and HCT116 cells treated with various concentrations of sorbitol or mannitol (25-300 mOsm) D., E. for the indicated times (0.5-6 h) F.-H. Representative gels are shown in D., F. and G.. Quantification of gel bands is shown in E. and H. (mean ± SEM, n = 3, *p < 0.05 vs. 0 mOsm or 0 h). HeLa cells were transfected with specific siRNAs against Beclin 1, ATG7 or VPS34, followed by infection with Ad GFP-LC3. Subsequently, cells were treated with 200 mOsm of sorbitol or mannitol for 0, 0.5, 1, 2 or 4 h. Autophagy was evaluated by fluorescent microscopy. The percentage of autophagic cells was quantified, shown in I. (*p < 0.05 vs. 0 h) and representative gels inserted in the graphic indicate the efficiency of siRNA downregulation for Beclin 1, ATG7 and VPS34 I. An unrelated siRNA (UNR) was used as a control. GAPDH and α-tubulin were used as loading controls J.-K. The effect of BafA1 treatment on LC3 I-to-LC3 II conversion and p62/SQSTM1 degradation under hyperosmotic stress conditions was assessed. HeLa cell cultures were exposed to sorbitol or mannitol (200 mOsm) for 0, 0.5 or 1 h in the presence or absence of 50 nM of BafA1. LC3 II and p62/SQSTM1 levels were then determined by Western blot analysis J.. GAPDH levels were monitored as a loading control. Quantification of gel bands is shown in K. (mean ± SEM, n = 3, *p < 0.05 vs. 0 h).
