Figure 4. Matriptase-cleaved Her2 CTFs have differential interaction with Herceptin.
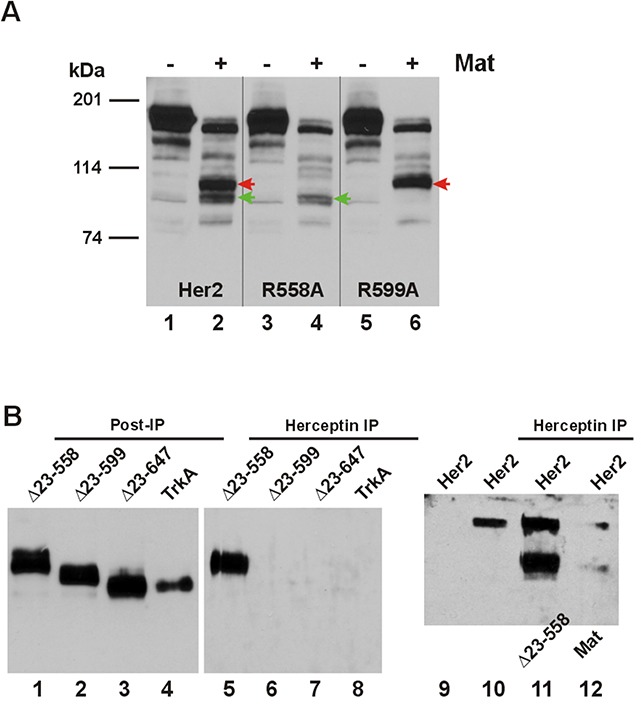
(A) The cDNA coding for a carboxyl-terminally HA-tagged wild-type Her2 or matriptase cleavage site mutant R558A or R599A was co-transfected in HEK293 cells with an empty plasmid (pcDNA3, Invitrogen) (Lane 1, 3, or 5), or the cDNA coding for human matriptase (Mat, Lane 2, 4, or 6). Twenty micrograms of total cell lysate from each sample were resolved on SDS-PAGE and western-blotted with an anti-HA antibody. The red arrowheads indicate the Her2 CTF resulting from matriptase cleavage at Arg558 and the green arrowheads indicate the Her2 CTF resulting from matriptase cleavage at Arg599. (B) The cDNA coding for amino-terminally truncated Her2s, Δ23-558, Δ23-599, or Δ23-647, or TrkA (all HA-tagged at the carboxyl terminus) was transfected in M17 human neuroblastoma cells, which were incubated with Herceptin for 24 hours. Immunoprecipitation (IP) and western blotting were performed as described in Materials and Methods. Samples from the IP were loaded in Lanes 5-8 and the post-IP samples were loaded in Lanes 1-4. The sample in Lane 9 was from cells not incubated with Herceptin, but the sample lysate was incubated with the agarose beads to serve as a negative control for the IP. The sample in Lane 11 was from cells co-transfected with the full-length Her2 and Δ23-558. The sample in Lane 12 was from cells co-transfected with the full-length Her2 and matriptase, as indicated. The sample in Lane 10 was from cells transfected with the full-length Her2 to serve as a positive control for the IP.
