Figure 1. Aurora kinase A colocalalizes with ARD1 during cell division and cell migration.
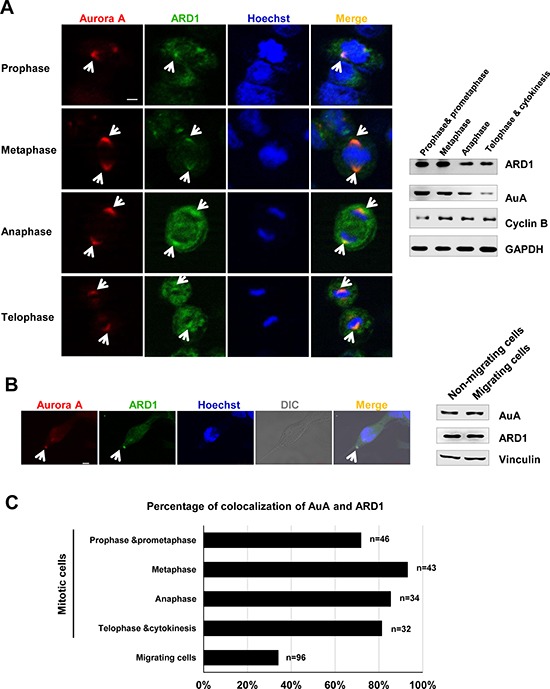
(A) Left, Aurora A colocalizes with ARD1 at centrosomes during cell division in prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. GFP-ARD1 overexpressing cells (green) were synchronized and stained with anti-AuA antibody (red). DNA was counter-stained by Hoechst. Cells were then viewed under a confocal microscope. Scale bar, 5 μm. Colocalization of ARD1 and AuA is indicated by arrows. Right, Expression of ARD1 and AuA during cell cycle progression. Cyclin B1 was used as the markers of the cell cycle phases. GAPDH was used as loading control. (B) Left, Aurora A colocalizes with ARD1 in migrating cell. Monolayer of GFP-ARD1 overexpressing cells (green) on coverslip was scratched to stimulate migration, then cells were stained with anti-AuA antibody (red). DNA was counter-stained by Hoechst. Scale bar, 5 μm. Colocalization of ARD1 and AuA is indicated by arrows. Right, Expression of ARD1 and AuA during cell migration. Vinculin was used as loading control. (C) The percentage of cells exhibit the colocalization of ARD1 and AuA during the cell cycle progression and cell migration.
