Figure 5. ARD1-mediated AuA acetylation enhances cell proliferation.
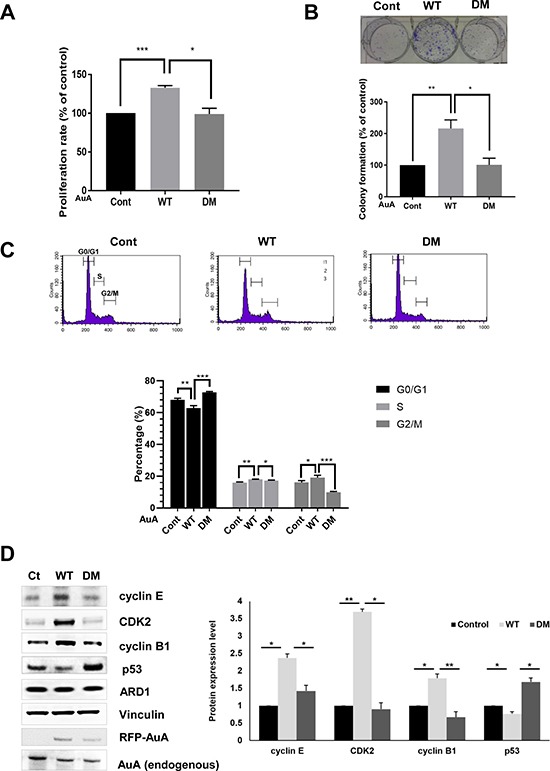
(A) Acetylation of AuA increases cell proliferation. The overexpressing RFP-AuA WT and RFP-AuA K75R/K125R MCF7 cells were seeded in 96-well plates and cultured for 48 h. Cells were then treated with MTT and measured absorbance at 490nm. ***p < 0.0005; *p < 0.05. Error bar indicates S.E.M (n = 3). (B) Acetylation of AuA promotes colony formation of MCF7 cells. The overexpressing RFP-AuA WT and RFP-AuA K75/125 MCF7 cells were seeded in 6-well plates and cultured for 7 days. Cells were then fixed with formaldehyde and stained with crystal violet to visualize colony formation for quantification. Representative image is shown. **p < 0.005, *p < 0.05. Error bar indicates S.E.M (n = 3). (C) The overexpressing RFP-AuA WT cells shows the decreased population in G0/G1 phase and increased number of cells in S phase and G2/M phase. RFP-AuA WT and RFP-AuA K75R/K125R overexpressing MCF7 cells were stained with propidium iodide and analyzed by BD Calibur flowcytometry. ***p < 0.0005; **p < 0.005; *p < 0.05. Error bar indicates S.E.M (n = 3). (D) Acetylation of AuA increases expression level of cyclin B1, cyclin E and CDK2, whereas decreases expression level of p53. Expression level of target proteins were analyzed by western blot and quantified by Image J program. Vinculin was used as loading control. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.005. Error bar indicates S.E.M (n = 3).
