Figure 5. The effect of C1orf64 on AR-mediated induction of PIP.
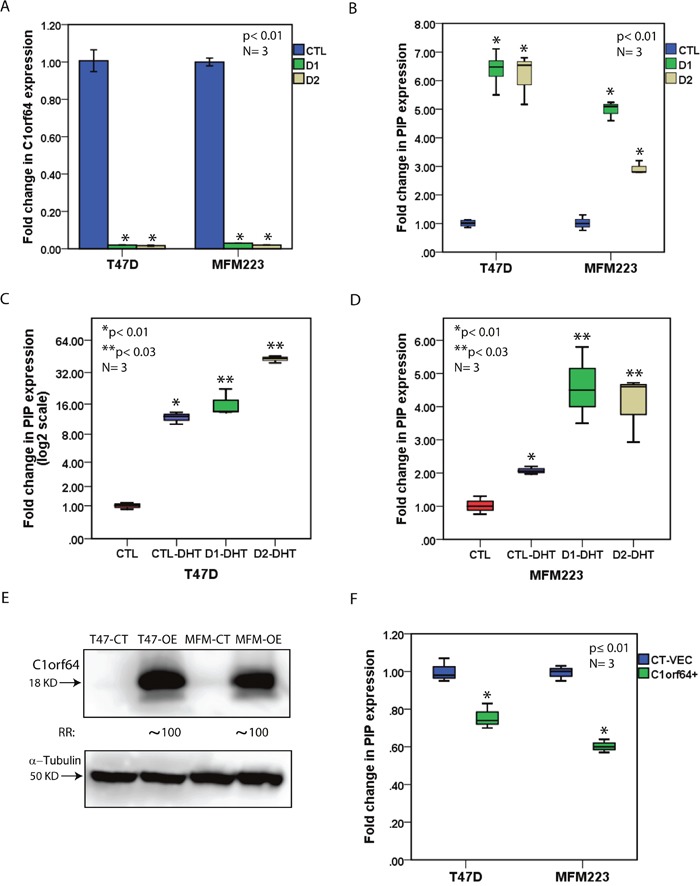
(A) qRT-PCR to demonstrate C1orf64 silencing efficiencies with siRNA-D1 (D1) and siRNA-D2 (D2) in T-47D and MFM-223 cell lines. C1orf64 expression is relative to non-targeting siRNA (CTL). *, p< 0.01 is for D1 or D2 vs. CTL. Error Bars: ± 2SEM. (B) qRT-PCR to show the effect of C1orf64 silencing using siRNA-D1 (D1) and siRNA-D2 (D2) on PIP expression in T-47D and MFM-223 cells. *, p< 0.01 is for D1 or D2 vs. CTL. (C) qRT-PCR to assess the effect of C1orf64 silencing on the DHT-mediated induction of PIP expression in T-47D cells. CTL: CTL-siRNA + solvent control, CTL-DHT: CTL-siRNA + DHT, D1-DHT: siRNA-D1 + DHT, D2-DHT: siRNA-D2 + DHT. *, p< 0.01 is for CTL vs. CTL-DHT and **, p< 0.03 is for CTL-DHT vs. D1-DHT or D2-DHT. (D) qRT-PCR to examine the effect of C1orf64 silencing on the DHT-mediated induction of PIP expression in MFM-223 cells as outlined in (C). (E) immunoblotting to assess C1orf64 protein levels in T-47D and MFM-233 cell lines following C1orf64 overexpression. Fold change (RR) in each band density was measured relative to control in three replicate experiments. CT: control vector, OE: overexpression. (F) qRT-PCR to assess the effect of C1orf64 overexpression on PIP expression in T-47D and MFM-223 cells. CT-VEC: Control vector, C1orf64+: C1orf64 overexpression. *, p≤ 0.01 is for CT-VEC vs. C1orf64+.
