Figure 3.
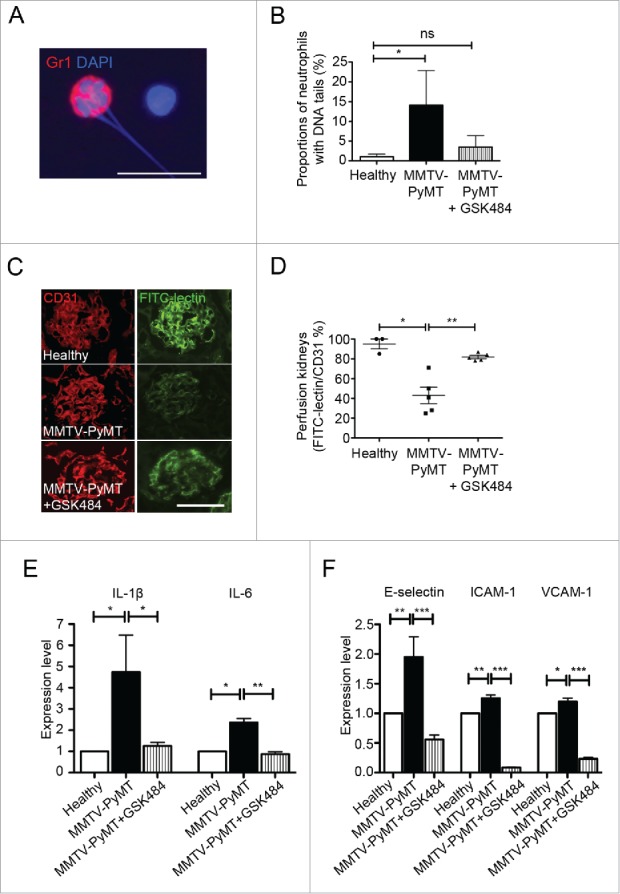
Pharmacological inhibition of PAD4 by GSK484 treatment improves perfusion and suppresses renal inflammation in kidneys from tumor-bearing mice. (A) Detection of neutrophils with extracellular DNA-tails in cytospin preparations of whole blood from MMTV-PyMT mice, by immunostaining for the neutrophil-associated marker Gr1 and DNA-staining with Hoechst. (B) Quantification of neutrophils with extracellular DNA-tails in peripheral blood from untreated and GSK484-treated MMTV-PyMT mice and healthy littermates (healthy, n = 4; MMTV-PyMT, n = 3; MMTV-PyMT + GSK484, n = 3). (C) FITC-lectin perfusion was used to analyze functionality of the renal vasculature in MMTV-PyMT mice with or without treatment with the PAD4-inhibitor. (D) Perfusion was quantified after immunostaining for the endothelial marker CD31, as the ratio FITC-lectin+/CD31+ area. Each data point corresponds to one individual mouse. (E) Kidney expression of the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and IL-6 was determined by qPCR. (F) Similarly, qPCR was used to measure the expression of the adhesion molecules E-selectin, ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 in kidneys. * = p < 0.05, ** = p < 0.01 and *** = p < 0.005. Scale bars correspond to 10 μm in A and 100 μm in B.
