Figure 1. 1q21 shRNA Screen Identifies ILF2 as a MM-Critical Gene.
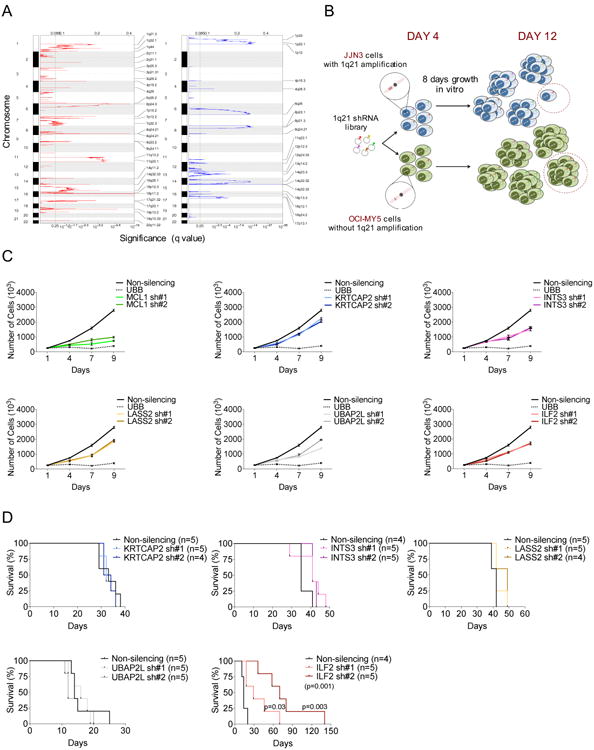
(A) GISTIC2 was used to identify chromosomal regions showing significant amplification (left) or deletion (right) in 254 MM patients. The green line indicates the significance threshold (q value of 0.25).
(B) Schematic representation of the screening strategy. A library of 532 GFP-positive shRNA vectors targeting the 78 amplified and overexpressed genes located in 1q21 and a GFP-competitive assay were used to identify genes whose loss of function resulted in the selective death and/or growth inhibition of MM cells carrying the 1q21 amplification (JJN3 cell line) but not MM cells without the 1q21 amplification (OCI-MY5 cell line) over a period of 8 days after the recovery from transduction.
(C) Representative growth curves of shRNA-transduced JJN3 cells. Every experiment was performed three times and included two different shRNAs per gene (sh#1 and sh#2), a non-silencing shRNA as a negative control, and an UBB-targeting shRNA as a positive control. All growth curves relative to each independent experiment were performed simultaneously (graphs were separated into six different panels). The mean and SD of duplicates from one representative experiment are shown.
(D) Survival curves of NOD/SCID mice injected subcutaneously with 1×106 shRNA-transduced JJN3 cells (n=4 or 5 mice per group as indicated). Survival curves were analyzed by Mantel–Cox log-rank test.
