Figure 6. ILF2-Mediated YB-1 Nuclear Translocation Regulates the Cotranscriptional Splicing of DNA Repair Transcripts in Response to DNA Damage.
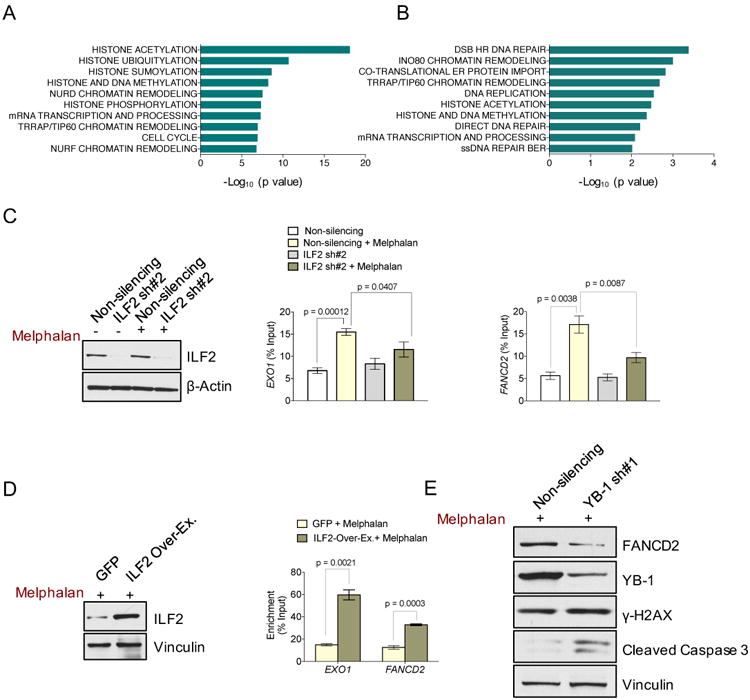
(A) Significantly enriched pathways relative to YB-1–bound transcripts in untreated JJN3 cells.
(B) Significantly enriched pathways relative to the transcripts whose binding to YB-1 was induced by melphalan treatment in JJN3 cells.
(C) Representative Western blot analysis of ILF2 in untreated and melphalan-treated non-silencing and ILF2 shRNA–transduced JJN3 cells. β-actin was used as the loading control (panel on the left). RIP-qPCR quantification of YB-1-bound EXO1 (middle panel) and FANCD2 (panel on the right) transcripts in untreated or melphalan-treated non-silencing and ILF2 shRNA-transduced JJN3 cells. The mean and SD of three independent experiments are shown; data are expressed as percentages of the corresponding input.
(D) Representative western blot analysis of ILF2 in GFP- and ILF2-overexpressing JJN3 cells. Vinculin was used as the loading control (panel on the left). RIP-qPCR quantification of YB-1–bound EXO1 and FANCD2 transcripts in melphalan-treated GFP-or ILF2-overexpressing JJN3 cells. The mean and SD of three independent experiments are shown; data are expressed as percentages of the corresponding input (panel on the right).
(E)) Western blot analysis of FANCD2, YB-1, γH2AX, and cleaved caspase 3 proteins in melphalan-treated non-silencing shRNA or YB-1 shRNA #1–transduced JJN3 cells. Vinculin was used as the loading control.
