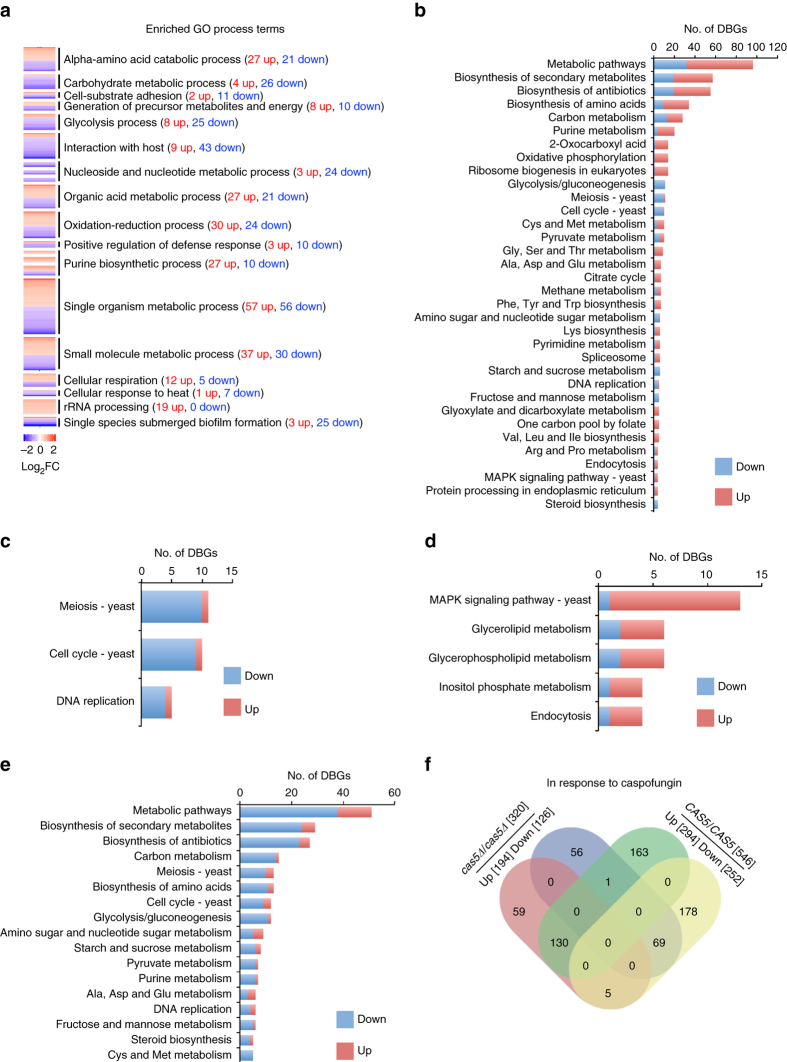
Fig. 1.
Cas5 has a profound impact on RNA PolII binding at genes implicated in cell wall and cell cycle processes under both basal and cell wall stress conditions. a Heat maps showing the genes with increased (red) and decreased (blue) RNA PolII binding in a cas5∆/cas5∆ mutant relative to wildtype. Enriched GO processes are indicated, and were clustered using the DAVID Gene Functional Classification Tool. b Bar chart showing the number of genes differentially bound by PolII (DBGs differentially bound genes), with increased binding in red and decreased binding in blue, in a cas5∆/cas5∆ mutant relative to wildtype based on their assigned KEGG pathways. KEGG pathways with four or more genes assigned are shown. c Bar chart showing the number of genes differentially bound by PolII, with increased binding in red and decreased binding in blue, in a cas5∆/cas5∆ mutant relative to wildtype belonging to select KEGG pathways involved in cell cycle and related processes. d, e Bar charts showing the number of differentially bound genes involved in the indicated physiological pathways upon caspofungin treatment, with increased binding in red and decreased binding in blue, in a wild-type strain in response to caspofungin. KEGG pathways were grouped according to the ratio of genes with increased PolII binding to genes with decreased PolII binding in response to caspofungin, with d enriched for genes with increased PolII binding and e enriched for genes with decreased PolII binding. KEGG pathways with five or more genes assigned are shown. f Venn diagram depicting number of genes differentially bound by RNA PolII in response to caspofungin in the wild-type reference (increased, green; decreased, yellow) and cas5Δ/cas5Δ mutant (increased, red; decreased, blue) strains. See Supplementary Data 1–4 for full data sets