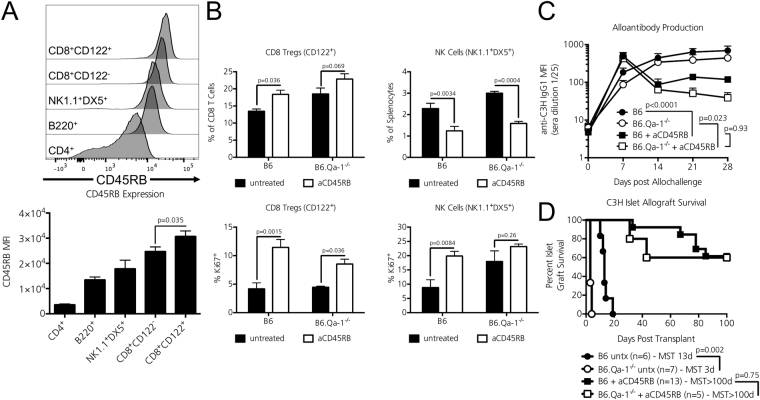
Figure 3.
Anti-CD45RB interacts with Qa-1 restricted cells but Qa-1 is dispensable for tolerance induction. (A) Expression of the CD45RB isoform on gated CD4+ T cells, B220+ B cells, NK1.1 + DX5 + NK cells, naïve CD122- CD8 T cells, and CD122 + CD8 Tregs was assessed by flow cytometry. Significance determined by One-way ANOVA for normally distributed data, followed by Tukey’s post-test for multiple comparisons. A significant p value is shown on the graph for two groups of interest. n = 3 mice per strain analyzed. (B) 12-week old B6 and B6.Qa-1−/− mice were left untreated or received a standard 7-day course of anti-CD45RB. CD8 Treg and NK cell populations were assessed on day 8. Overall, anti-CD45RB significantly increased CD8 Treg frequencies and proliferation (as measured by Ki-67 positivity) in both strains. Although this agent significantly reduced splenic NK cell frequencies in both strains, anti-CD45RB significantly increased NK cell proliferation in B6 mice. Data shown is pooled from two independent experiments (n = 3–7 mice per strain analyzed). Significance determined by two-way ANOVA, followed by Bonferroni’s post-test. Adjusted p values of interest are shown on the graph. (C) 12-week old B6 and B6.Qa-1−/− mice (H2-b) were i.v. injected with 30 million fully-MHC mismatched C3H splenocytes (H2-k) and left untreated or received 100 ug i.p. injections of the tolerance inducing agent anti-CD45RB on days 0,1,3,5,7 relative to allochallenge (d0). Mice were bled weekly and anti-C3H IgG1 alloantibody titers analyzed by flow cytometry using target C3H cells. Overall, anti-CD45RB therapy significantly reduced anti-C3H IgG1 alloantibody production in both B6 and B6.Qa-1−/− recipients vs. their untreated counterparts. There was no significant difference in anti-C3H IgG1 alloantibody titers between anti-CD45RB treated B6 and B6.Qa-1−/− recipients. n = 4–5 mice per strain analyzed, pooled from two independent experiments. Significance determined by two-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey’s post-test. Adjusted p values of interest comparing Day 28 are shown on the graph. (D) STZ treated, diabetic B6 and B6.Qa-1−/− recipients were transplanted with fully MHC-mismatched C3H islet allografts and administered 100ug i.p. injections of the tolerance inducing agent anti-CD45RB on days 0, 1, 3, 5, 7 relative to the day of transplantation (d0). Overall, the absence of Qa-1 did alter the susceptibility to long-term transplant tolerance induction. Animals achieving 100 days of tolerance were nephrectomized of their allograft-containing kidneys. All animals returned to hyperglycemia within 2 days of surgery confirming graft function for maintenance of euglycemia (not shown). Significance determined by Log-Rank test. p values are shown on graph and the number of graft recipients is denoted by n on the graph.