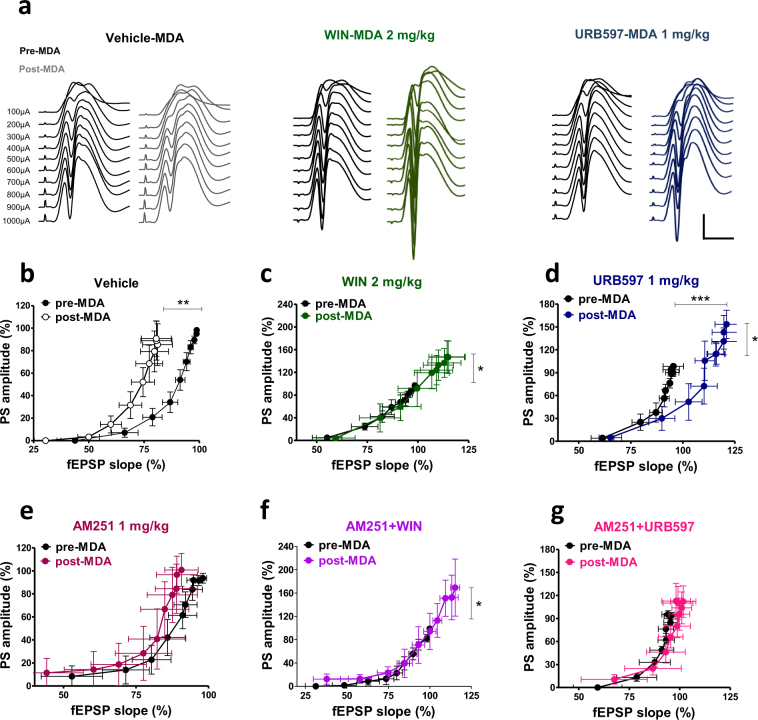
Figure 7.
Effects of peripheral administration of cannabinoid compounds on basal synaptic plasticity and cellular excitability assessed in control (pre-MDA, drug free condition) and in post-MDA condition. (a) Representative DG field potential responses obtained with stimulation intensities ranging from 100 through 1000 μA, recorded before MDA (drug free condition) and after MDA in presence of vehicle (vehicle-MDA), WIN 2 mg/kg (WIN-MDA) and URB597 1 mg/kg (URB597-MDA). Scale bar = 2 mV and 5 MDA acute kindling caused a significant left-ward shift of the I/O curve in vehicle treated animals (b) which was prevented by the administration of WIN and URB597 (c and d). The left-ward shift of the I/O curve is still present in the AM251-MDA group but no longer significant (e). AM251 did not prevent the effect of WIN and only partially prevented the effect of URB597 in the I/O curve (f and g, respectively). One-way ANOVA for repeated measures followed by Bonferroni post hoc test; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 versus pre-MDA condition group.