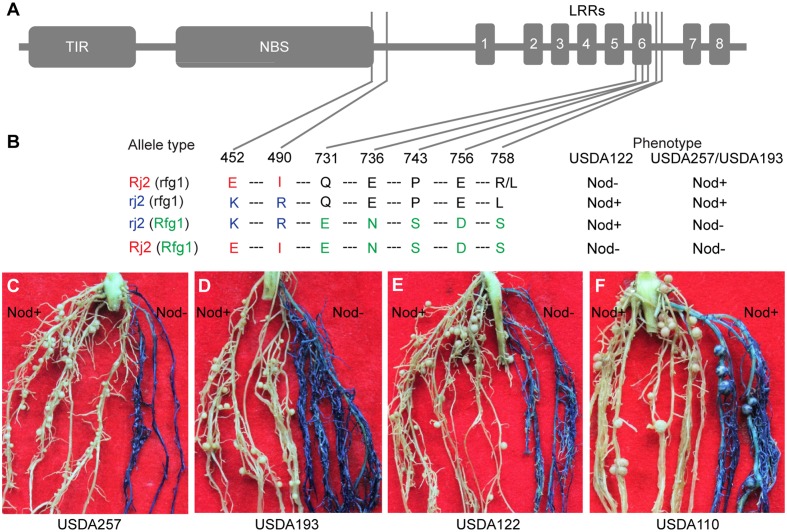
FIGURE 4.
Functional analysis of a chimeric gene of Rfg1 and Rj2. (A,B) Domain structure of the TIR-NBS-LRR protein (A) showing the seven substitution sites and amino acid polymorphisms that distinguish between the Rj2 (rfg1), rj2 (rfg1), and rj2 (Rfg1) protein isoforms (B). Rj2 (Rfg1) represents a protein isoform resulting from expressing the chimeric gene. (C–F) Transgenic roots expressing the chimeric gene (blue) in the Peking background restricted nodulation by USDA257 (C), USDA193 (D), and USDA122 (E) but allowed nodulation with B. japonicum USDA110 (F). In all cases, the nodulation was normal on the non-transgenic roots (white).