FIGURE 1.
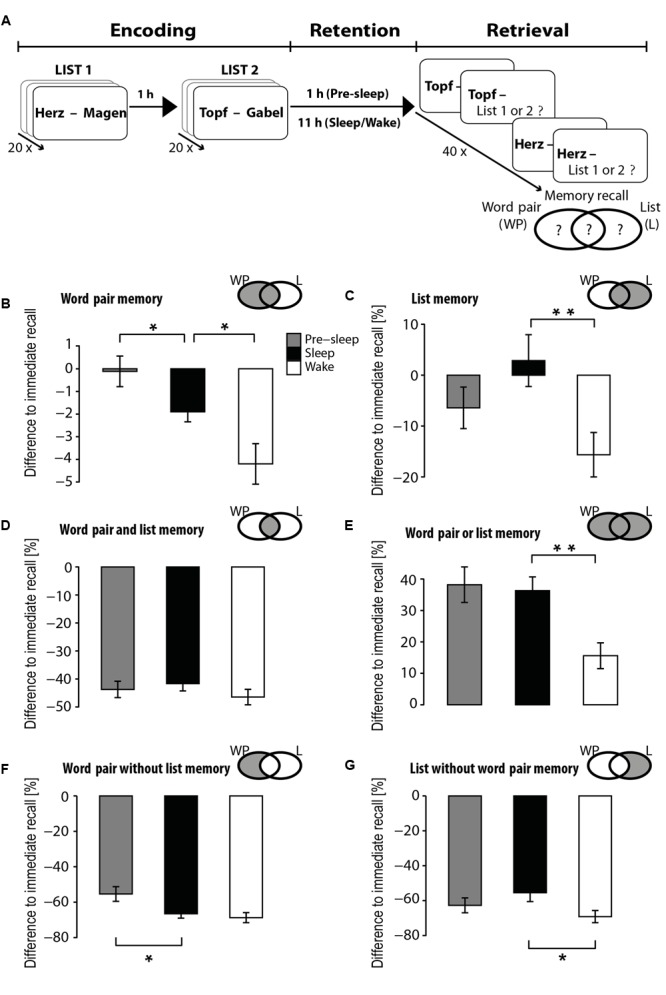
Experimental design and memory dynamics in children. (A) The Encoding phase of the experiment consisted of learning two lists of word pairs, each studied once 1 h apart. The duration of the retention interval was either 1 h (Pre-sleep condition) or 11 h with the latter including either a night of sleep (Sleep condition) or daytime wakefulness (Wake condition). In the retrieval phase cued recall was tested for each word pair followed by a recall of the list (forced choice between List 1 and 2) in which the word pair had appeared. Each recall trial was categorized according to the correctness of the associated target word (WP) or the associated list (L) as depicted in the grayed area of Venn diagrams next to the bar graphs. (B–G) Children’s mean (± SEM) cued recall performance for the Pre-sleep (gray bars), Sleep (black) and Wake (white) conditions for (B) correctly recalled word pairs, (C) correctly recalled lists, (D) trials with both correctly recalled word pairs and lists, (E) trials with correctly recalled word pairs or lists or both, (F) trials with correctly recalled word pairs but incorrect list recall, and (G) trials with correct list recall but incorrect word pair recall. Recall is expressed as the difference from immediate recall of word pairs during the encoding phase. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, for pairwise comparisons between retention conditions.
