FIGURE 1.
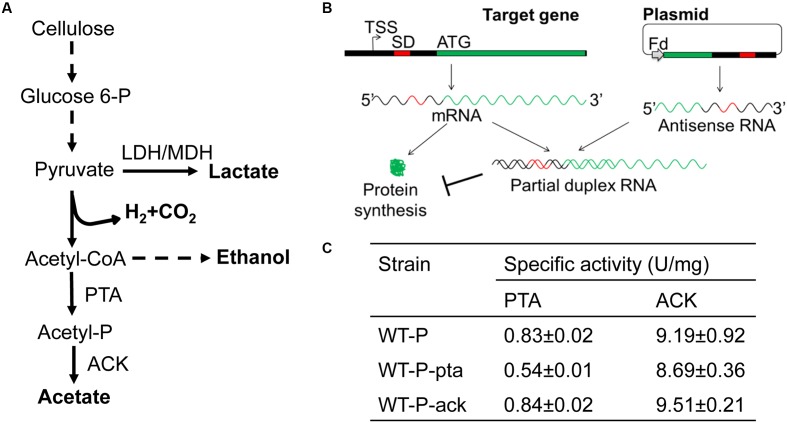
(A) Major metabolic pathways in C. cellulolyticum. Acetyl-CoA as a key intermediate metabolite, apart from being used to produce ethanol, can be converted to acetyl-phosphate by phosphotransacetylase (PTA, encoded by pta gene) and then to acetate by acetate kinase (ACK, encoded by ack gene). L-lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and L-malate dehydrogenase (MDH) are functional in one-step lactate production from pyruvate. Dashed arrows refer to multiple enzymatic reactions. (B) Design of antisense RNAs (asRNAs) to repress pta and ack genes. For each target gene, the transcriptional region spanning from the predicted transcriptional start site (TSS) to the downstream site approximately 120-bp from the start codon (ATG), containing the Shine-Dalgarno sequence (SD), was amplified and reversely inserted downstream of the ferredoxin (Fd) promoter, generating the Fd::asRNA module. AsRNAs would interfere with the transcription, stability and translation of the target gene. (C) Enzyme assays of PTA and ACK in crude cell-free extracts. Mean and standard deviations of specific enzyme activities were calculated from three biological replicates.