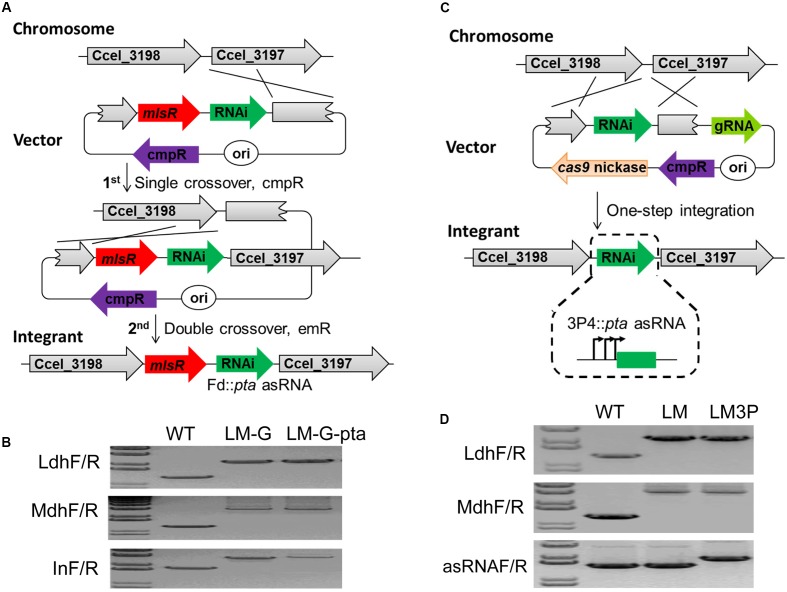
FIGURE 3.
Chromosomal integration of functional modules via double-crossover recombination (A,B) and the Cas9 nickase genome editing tool (C,D). The integration site was located in the intergenic region between Ccel_3198 and Ccel_3197. (A) Generation of stable double-crossover clones, LM-G and LM-G-pta, using pLyc045 and pLyc046, respectively. The first step was to screen thiamphenicol-resistant single-crossover clones generated by plasmid integration. The second step was to select erythromycin-resistant double-crossover clones as a result of plasmid excision. Finally, modified genomic loci in candidate clones were verified by PCR with specific primers, LdhF/R for Δldh identification, MdhF/R for Δmdh identification and InF/R for module integration (B). (C) Generation of stable chromosomal integrants, LM3P and LM3PS, by the Cas9 nickase genome editing tool. By transforming pCas9n-3198D-donor into the LM mutant, integrants were generated within a single step. (D) Modified genome loci in all integrants were then verified by PCR with specific primers, asRNAF/R for RNAi module integration. LM is a double mutant (Δldh Δmdh); LM-G-pta and LM3P are triple mutants (Δldh Δmdh Δpta).