Figure 2.
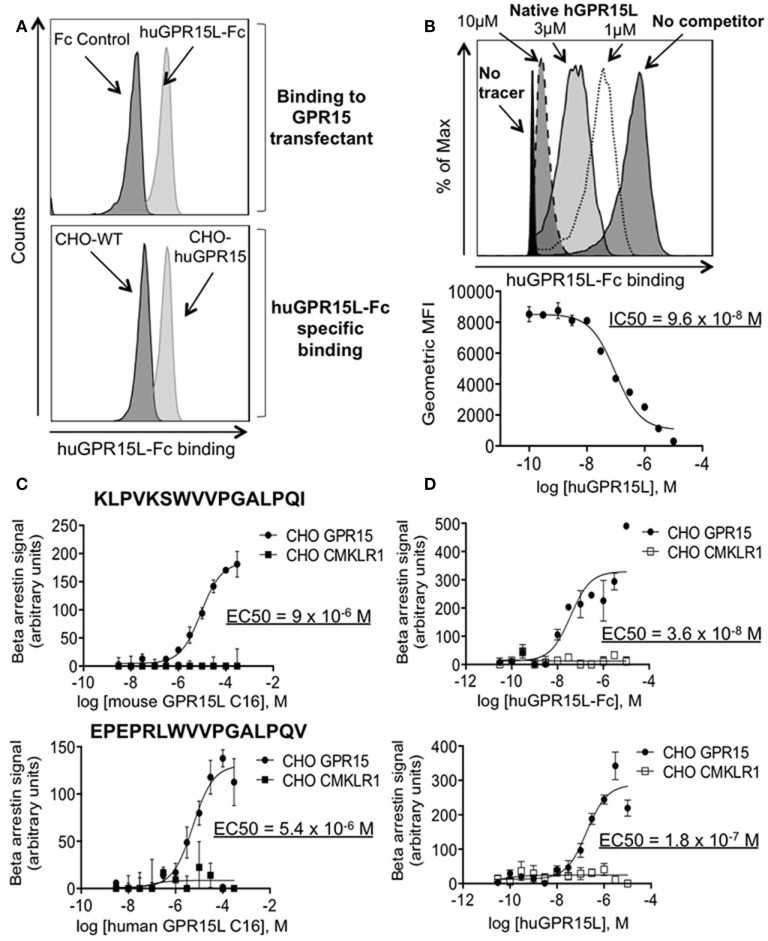
GPR15L binds specifically and is an agonist for GPR15. (A) Top panel; histogram showing binding of human GPR15L-Fc (0.1 nM) chimeric protein to CHO-K1 cells expressing human GPR15. Bottom panel; histogram showing specific binding of the GPR15L (0.1 nM) chimeric protein to GPR15 transfectants. (B) Representative histogram and graph showing the reduction in the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) given by the human chimeric protein binding (tracer) (1 nM), due to the concentration-dependent competition of the human native GPR15L. (C) β-arrestin assay using CHO-huGPR15 reporter cells and CHO-huCMKLR1 as internal control, with the C-terminal peptide of the mouse GPR15L (top panel) and human GPR15L (bottom panel), containing the activating peptide. The sequences of each peptide are highlighted in bold letters on each graph. (D) β-arrestin assay using CHO-huGPR15 reporter cells and CHO-huCMKLR1 as internal control, with human GPR15L-Fc chimeric (top panel), and native human GPR15L (bottom panel) full-length proteins. IC50 = half maximal inhibitory concentration; EC50 = half maximal effective concentration. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, n = 3 for each condition and representative of three independent experiments.