Fig. 1.
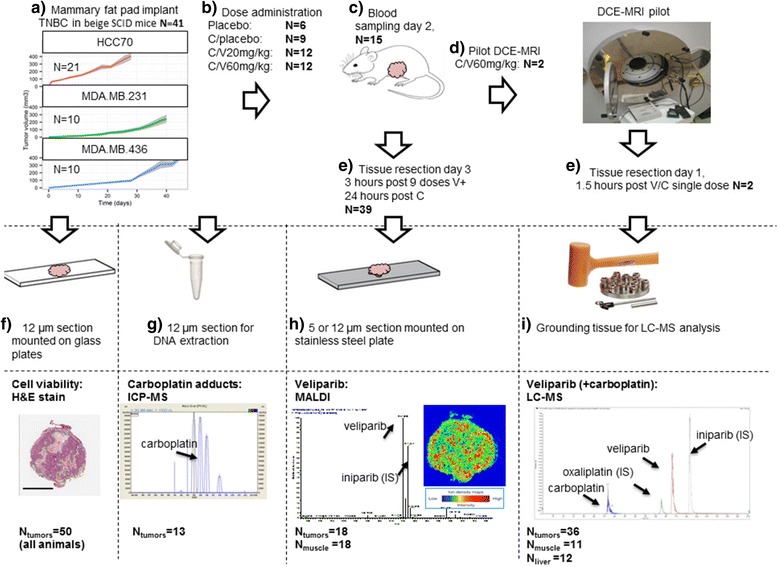
Study design. a Forty-one beige DF mice with severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) were implanted with 106 MDA-MB-231 (N = 10), HCC70 (N = 21) or MDA-MB-436 (N = 10) triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells bilaterally in the mammary fat pads and grown to at least 200 mm3. b The mice were then randomized across the treatment cohorts. Veliparib (V) (20 mg/kg; low dose (N = 12) or 60 mg/kg; high dose (N = 12) or placebo (N = 9)) was administered per oral gavage three times daily for 3 days (c). Carboplatin (C) 60 mg/kg (N = 33) or placebo (N = 6) was administered via intravenous injection on days 1 and 2. Blood samples were taken on day 2 at 0.6, 3 and 5 h after veliparib and carboplatin dosing of 15 mice. d In two mice the TNBC tumors were further analyzed using dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) after the first dose (N = 2). e Mice were euthanized on day 3, at 3 h after the last dose of veliparib (N = 39), or at 1.5 h after single-dose V/C (N = 2 (DCR-MRI pilot). Bilateral xenograft tumors and liver and muscle (quadriceps) tissues were obtained. Tissues were divided into three parts and cryo-sectioning was performed in one part. Serial 5-μm-thick or 12-μm-thick sections from each biopsy were cut. H&E staining (f), matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometric imaging (MALDI-MSI) (veliparib) (h) and ICP-MS (platinum adducts) (g) were performed on subsequent sections of veliparib/carboplatin-treated animals. i One part of the tissue was ground for quantification using LC-MS
