Fig. 4.
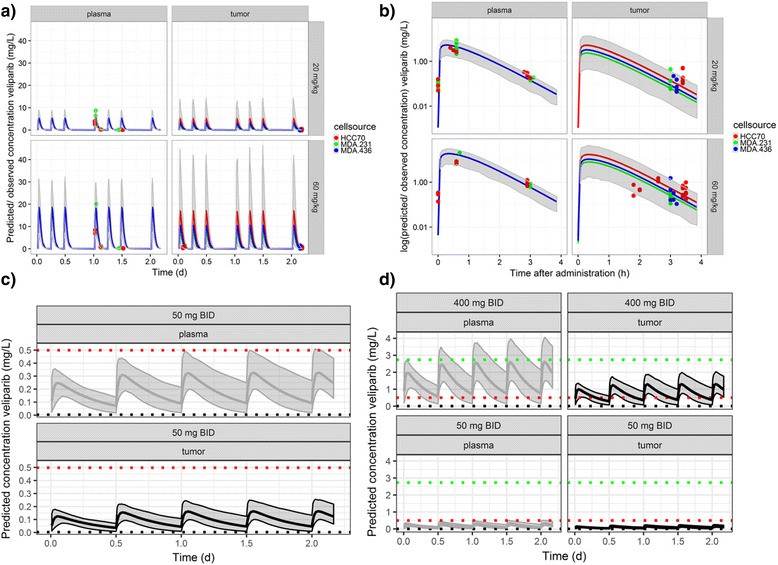
Observed and the associated model-predicted plasma and tumor (LC-MS derived) concentrations at 3 days (a) and after the last veliparib administration (b) show that the pharmacokinetic (PK) model (shaded area shows 95% CI prediction interval and the straight line shows the typical PK profile) of the xenograft mouse data is able to reproduce the central tendency in the observed plasma and xenograft veliparib concentrations (dots, colored by TNBC xenograft cell line). c Simulation of plasma and tumor concentrations in patients show that plasma and tumor exposures in the mice treated with 20 mg/kg veliparib are similar to patient exposures after 50 mg twice daily (BID) dosing. The line represents the typical PK profile and shaded areas are the simulated median with 95% CI uncertainty of the simulated concentrations in plasma (gray) and tumor (black). d Comparison of the simulated concentrations with in vitro derived half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values observed in breast cancer cells suggests that concentrations at steady state of veliparib 400 mg BID may be sufficient for patients with a somatic or germline BRCA mutation (using IC50 values observed in BRCA mutated breast cancer cells, red dotted line), but may be below the effective concentration in non-BRCA carriers (using IC50 values observed in non-BRCA mutated breast cancer cells, green dotted line)
