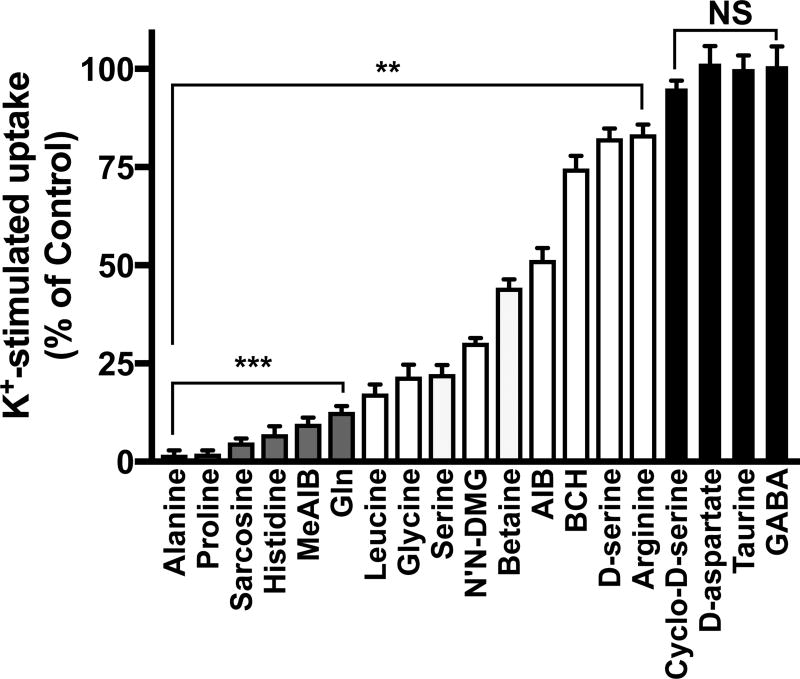
Fig. 5. Substrate competition profiles for Ca2+-dependent, high affinity 14C-MeAIB transport.
Cultures are exposed to high K+ (60 mM plus 1.2 mM CaCl2) for 5 min at 37°C, then are rinsed in N buffer, and 14C-MeAIB (20 µM) uptake is performed in N buffer (5 min, 37°C). Transport is conducted in the absence or presence of various amino acid competitive substrates (2 mM). Uptake values obtained at 4°C were less than 5% and were subtracted. Subtracted data were normalized to 14C-MeAIB uptake in the absence of unlabeled amino acids. N’N-DMG, N’N dimethylglycine. AIB, aminoisobutyric acid. BCH, 2-amino-2-norbornane-carboxylic acid. Cyclo-D-ser, cyclo-D-serine. Data are the mean +/− S.E. values from n=3–5 independent experiments. **p < 0.01, indicates significant differences from uptake in the absence of unlabeled substrate. ***p < 0.01) indicate amino acids (ala, pro, sarcosine, his, MeAIB, Gln) that reduce 14C-MeAIB transport by greater than 90%. N.S., not significant.