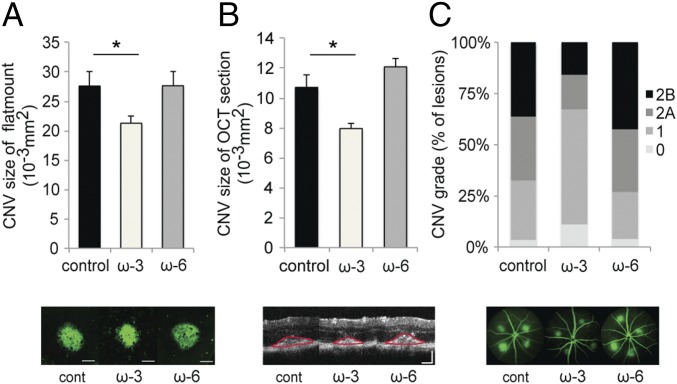
Fig. 2.
Dietary intake of ω-3 LCPUFAs in sEH null mice attenuates CNV. (A and B) Lesion size at 7 d after CNV induction was assessed by staining of choroidal flat-mount preparations with fluorescent isolectin B4 (A) and a cross-sectional area of lesions was quantified by SD-OCT (demarcated by red lines) (B), for sEH null mice fed a control diet (n = 49 lesions, respectively), ω-3 LCPUFA-enriched diet (n = 57 lesions, respectively), or ω-6 LCPUFA-enriched diet (n = 50 lesions, respectively) beginning 2 wk before laser photocoagulation. sEH null mice lack expression of sEH, an enzyme that degrades CYP-dependent epoxynoid fatty acid metabolites into less bioactive vic-diols. ω-3 LCPUFAs decreased CNV size in choroidal flat-mount and OCT section compared with the control diet and ω-6 LCPUFA-diet groups. Data are presented as means ± SEM. *P < 0.05. (Scale bar: 100 μm.) (C) Fluorescein leakage in CNV lesions was graded at 7 d after CNV induction in sEH null mice fed a control diet (n = 49 lesions), ω-3 LCPUFA-enriched diet (n = 57 lesions), or ω-6 LCPUFA-enriched diet (n = 50 lesions) beginning 2 wk before laser photocoagulation. ω-3 LCPUFAs also attenuated fluorescein leakage from the CNV lesions compared with the control diet and ω-6 diet groups. The grade of the hyperfluorescent lesions is as follows: score 0 (i.e., no leakage); score 1 (i.e., debatable leakage); score 2A (i.e., definite leakage); score 2B (i.e., clinically significant leakage).