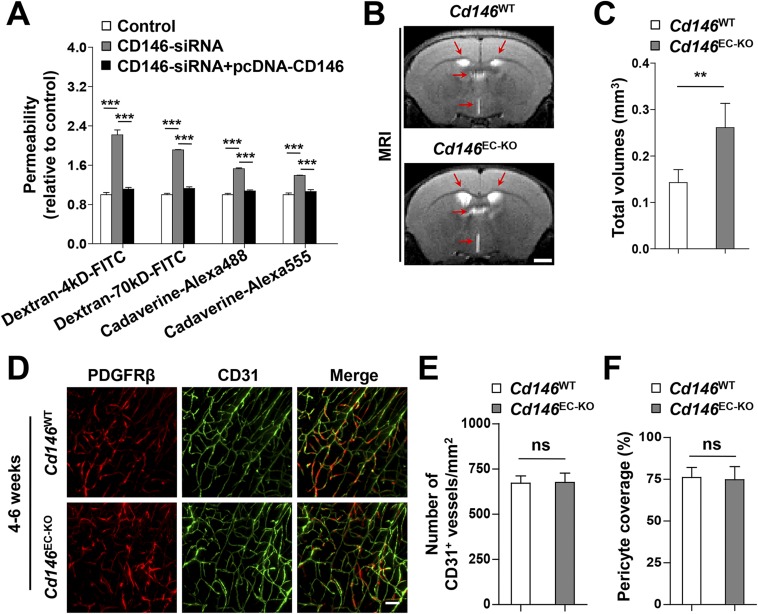
Fig. S4.
Deletion of endothelial Cd146 leads to BBB breakdown and enlargement of brain ventricles. (A) hCMEC/D3 cells were transfected with CD146 siRNA or cotransfected with CD146 siRNA and CD146-expressing plasmid. The paracellular permeability was assessed by using fluorescent tracers of different sizes of dextrans (4 kDa and 70 kDa) and cadaverine (640 Da and 950 Da; n = 10 per group). (B) Representative images at the same brain level were chosen from the volumes aligned to the Waxholm space. T2-weighted coronal MRI scans showing enlargement of the ventricles (red arrows) in Cd146EC-KO mice compared with that in Cd146WT mice at 4–6 wk. (Scale bar: 1,000 μm.) (C) Quantification of the total volumes of ventricles, including left lateral ventricle, right lateral ventricle, third ventricle, and fourth ventricle in Cd146EC-KO mice and Cd146WT mice at 4–6 wk. (D) Brain sections from cortex of mice at 4–6 wk were costained for CD31 (green) and PDGFRβ (red) and analyzed by LSFM after being optically cleared by using organic solvents. Representative MIPs of 40 virtual single slices from Cd146WT and Cd146EC-KO mice are shown. (Scale bar: 50 μm.) (E) Quantification of the number of CD31+ capillaries of brain cortex from Cd146WT and Cd146EC-KO mice. No difference was detected. (F) Pericyte coverage was quantified by analyzing percent length of CD31+ capillaries opposed to PDGFRβ+ pericytes. No difference was detected (**P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001). Data are from one experiment representative of three independent experiments with eight mice per genotype (C) or five mice per genotype, at least eight MIPs per mouse, and five random fields per MIP (E and F).