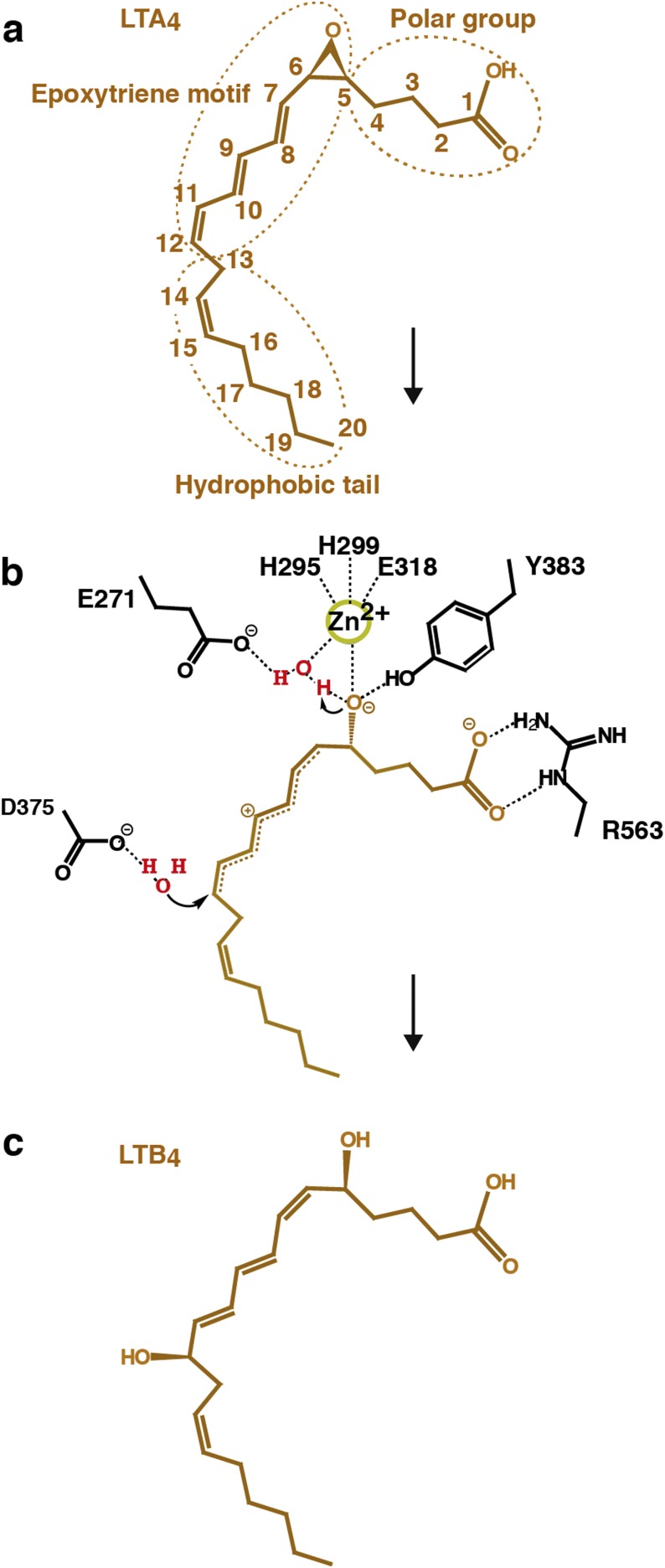
Fig. S1.
Proposed mechanism for enzymatic conversion of LTA4 into LTB4. (A) Chemical structure of LTA4. (B) Formation of a carbonium intermediate after SN1 acid-induced opening of the epoxide moiety. During the reaction, one catalytic water assists in the opening of the epoxide moiety, and the second catalytic water is responsible for the stereospecific insertion of an (R)-hydroxyl group at C12 of the carbonium ion. This process, together with rearrangement of the geometry of the conjugated triene system leads to formation of the bioactive LTB4. (C) Chemical structure of LTB4.