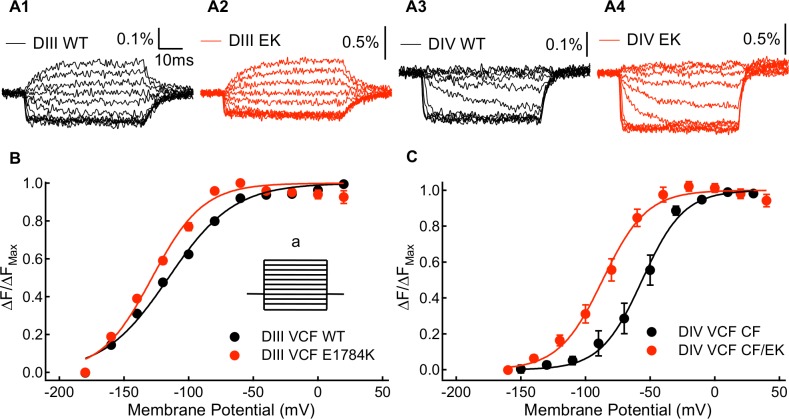
Fig 5. Kinetic and steady-state properties of fluorescence signals from the WT-DIII-VCF, E1784K-DIII-VCF, WT-DIV-VCF, and E1784K-DIV-VCF constructs.
(A1-A4) Representative fluorescence signals for DIII-VCF, E1784K-DIII-VCF, DIV-VCF, and E1784K DIV-VCF constructs. Percentage of fluorescence change were calculated as ΔF/F0. (B) Voltage-dependence of steady state fluorescence signal change (FV) of WT-DIII-VCF and E1784K-DIII-VCF constructs. The E1784K mutant causes a shift in the DIII FV curve to more hyperpolarized membrane potentials. (B inset) To measure the voltage-dependence of voltage-sensor fluorescence, the membrane potential of cells was changed to between -180mV and +20mV (a) from a holding potential of -120mV. (C) Voltage-dependence of steady state fluorescence signal change (FV) of WT-DIV-VCF and E1784K-DIV-VCF constructs. The E1784K mutant shifts the DIV FV curve in the hyperpolarizing direction.