Fig. 2. The effects of GA treatment on motor behavior in N171-82Q transgenic mice.
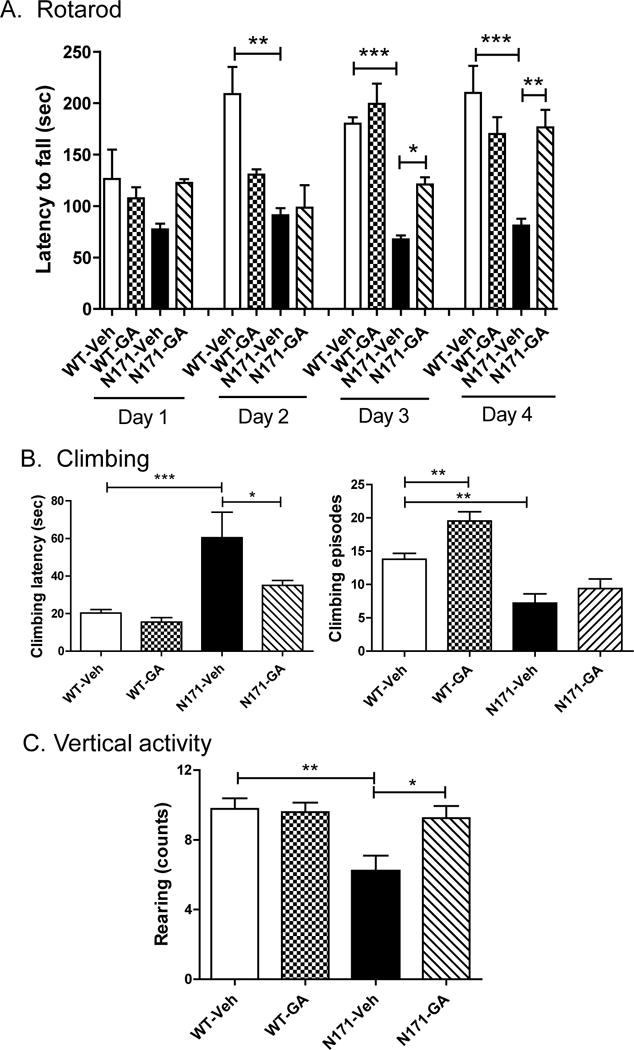
A). Rotarod was measured over four days at 15 weeks of age using an accelerating paradigm. The mean ± S.E.M. level of performance for each group of WT and N171-82Q transgenic mice (n=5–6 per group, males only) on each day is shown. Panel B shows the effects of GA treatment on climbing activity of WT and N171-82Q transgenic mice 17 weeks of age. Bar graphs depict mean +/− S.E.M. performance from n=8–10 mice per group. Panel C depicts the effects of GA on vertical activity of WT and N171-82Q transgenic mice (n=8–10 per group) at 18 weeks of age. Bar graphs depict mean +/− S.E.M. performance from n=8−10 mice per group. Significant differences were determined by One-way ANOVA, followed by Dunnett’s post-test. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001.
