Figure 2.
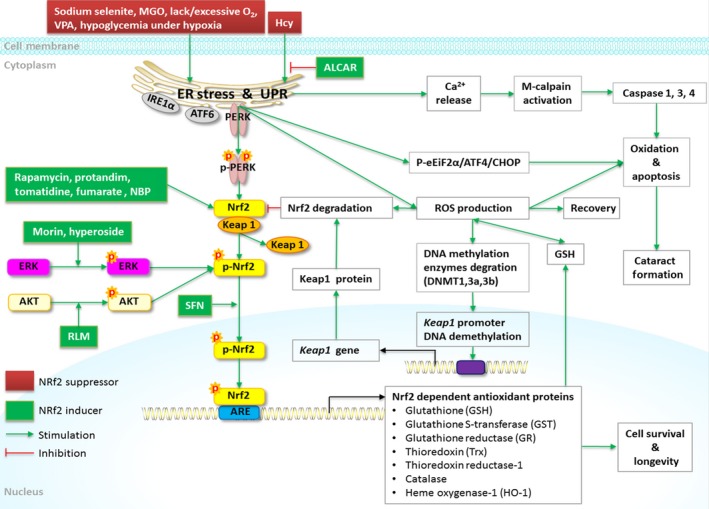
Nrf2 signaling and regulation in the lens. Various cataractogenic stressors induce ER stress, UPR activation, P‐PERK expression, and Nrf2 phosphorylation. The phosphorylated Nrf2 separates from Keap1, binds with ARE in the nucleus, and initiates the antioxidant enzymes transcriptions (GSH, GST, GR, Trx, thioredoxin reductase‐1, catalase, HO‐1), which help eliminating ROS by regenerating GSH. Severe or prolonged ER stressors (sodium selenite, Hcy, VPA, lack/excessive O2, hypoglycemia under hypoxia) cause chronic apoptotic UPR and ROS overproduction, ER‐Ca2+ release, calpain overexpression, and caspase 1,3,4 pathways’ activation, leading to the lens oxidation and cell death. Chronic apoptotic UPR also suppresses the Nrf2‐dependent antioxidant protection resulting in cataract formation. Hyperoside, morin, acetyl‐l‐carnitine, DL‐3‐n‐butylphthalide, RLM activate Nrf2 and protect lenses from oxidation. Excessive ROS also inhibit the Nrf2‐dependent antioxidant system via accelerating the DNA methylation enzymes degradation, triggering demethylation of DNA in the Keap1 promoter and overexpression of Keap1, which enhances the Nrf2 proteasomal degradation. Rapamycin, protandim, tomatidine, fumarate activate the Nrf2 signaling and extend the life longevity. Green solid line indicates direct stimulation. Red solid line indicates direct inhibition. ROS, reactive oxygen species; Nrf2, transcription factors like nuclear factor (erythroid‐ derived 2)‐like 2; Keap1, Kelch‐like erythroid‐cell‐derived protein with CNC homology (ECH)‐associated protein 1; ARE, antioxidant response element; GST, glutathione‐S‐transferase; GR, glutathione reductase; p‐PERK, phosphorylated protein kinase RNA (PKR)‐like endoplasmic reticulum kinase; UPR, unfolded protein response; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; Hcy, homocysteine; Trx, thioredoxin; GSH, glutathione; VPA, valproic acid; ALCAR, acetyl‐l‐carnitine; p‐eIF2α, phosphorylated eukaryotic initiation factor 2α; IRE1α, Inositol‐requiring kinase 1α; ATF6, transcription factor 6; ATF4, activating transcription factor 4; CHOP, CCAAT/enhancer‐binding protein‐homologous protein; Dnmt3a, DNA methyltransferase 3a; Dnmt3b, DNA methyltransferase 3b; Dnmt1, DNA methyltransferase 1; HO‐1, heme oxygenase‐1; ERK, extracellular signal‐regulated kinase; SFN, sulforaphane; NBP, DL‐3‐n‐butylphthalide; MGO, methylglyoxal; RLM, Rosa laevigata Michx.; AKT, serine–threonine kinase.
