Figure 6.
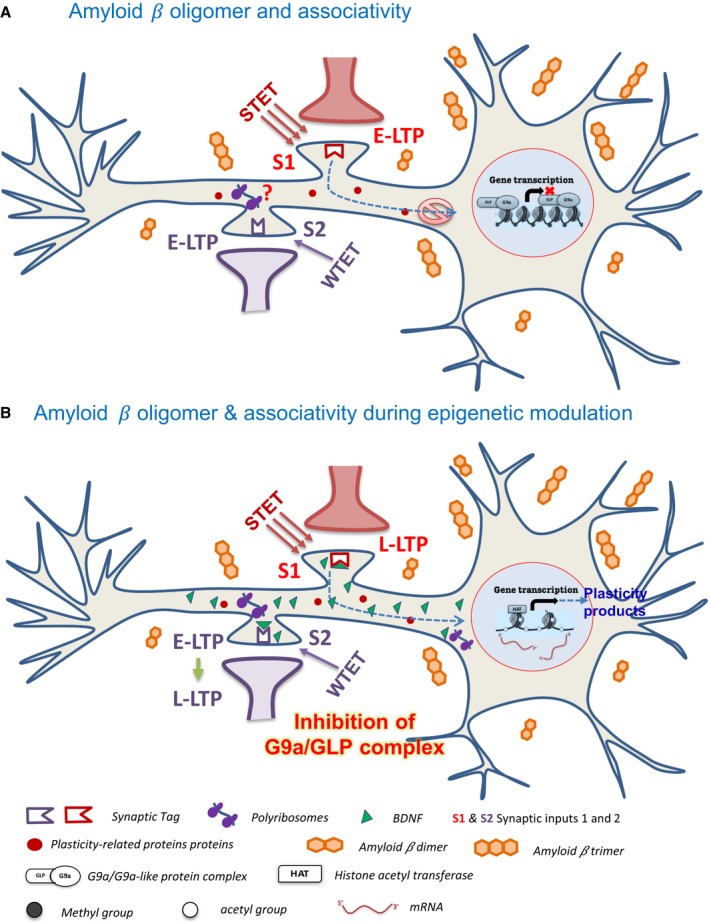
Schematic model representing the rescue of Amyloid β‐oligomer‐induced deficits in associative plasticity by inhibition of G9a/GLP complex. (A) The neuron when exposed to amyloid β oligomer, application of STET, marks the synapses (synaptic input 1, S1) with a synaptic ‘tag’ but fails to induce protein synthesis. The scarcity of plasticity proteins required for maintenance results in an early‐LTP. The subsequent induction of WTET in the neighboring synapses (S2) leads to an early‐LTP as well because of dearth of ‘plasticity proteins’ to be captured by the tagged synapses, resulting in the deficits in synaptic tagging/capture. Increased G9a/GLP activity is one of the contributing factors toward the malfunctioning of protein synthesis machinery during the presence of Aβ oligomer. G9a/GLP complex methylate the histones (H3K9me2) and nonhistone targets. H3K9me2 marks prevent the gene transcription by retaining the condensed form of chromatin that is inaccessible to the transcription machinery. This further interferes with the translation process of plasticity‐related proteins. (B) The pharmacological inhibition of G9a/GLP complex either by UNC0638 or BIX 01294 will prevent this complex from binding the histones and their subsequent methylation is intercepted. This will facilitate the binding of histone acetyl transferases (HATs), thereby resulting in the unwinding of DNA and rendering it accessible to the transcription machinery. This is followed by the increased expression of plasticity genes like Bdnf. The resulting upsurge in the translation process of plasticity‐related proteins like BDNF, which binds to TrkB receptor and activates downstream signaling pathways, paves the way to late‐LTP expression. The global distribution of BDNF and other plasticity proteins will enable the active set of synapses (S1 and S2) to ‘capture’ these proteins, resulting in a stable plasticity and late associativity. Additionally, the local synthesis of BDNF might be upregulated as well which further results in its profusion in the neuron. BDNF = brain‐derived neurotrophic factor; HAT = histone acetyltransferase; G9a/GLP = G9a/G9a‐like protein complex.
