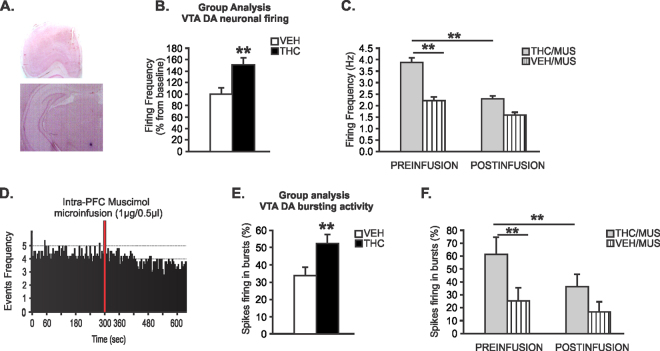
Figure 5.
Effects of Intra-mPFC MUS on adolescent THC-induced sub-cortical hyperdopaminergia. (A) microphotograph of a representative mPFC microsyringe and VTA neuronal recording placements. (B) Increased VTA putative DA neuronal firing frequency in adolescent THC-pretreated rats relative to adolescent VEH-pretreated rats. (C) Before intra-mPFC MUS microinfusion, sub-population of VTA putative DA neurons firing frequency in adolescent THC pretreated rats were significantly increased compared to adolescent VEH pretreated rats. Intra-mPFC MUS reduced firing frequency of VTA putative DA in adolescent THC-pretreated rats relative to adolescent VEH-pretreated rats. (D) Representative rastergram showing the spontaneous activity of 1 putative DA neuron treated with intra-mPFC muscimol in adolescent THC pretreated rat. (E) Increased VTA putative DA neurons bursting levels in adolescent THC vs. VEH pretreated rats. (F) Before intra-mPFC MUS microinfusion, sub-population of VTA putative DA neurons spikes firing in bursts in adolescent THC pretreated rats were significantly increased compared to adolescent VEH pretreated rats. Intra-mPFC MUS reduced spikes firing in bursts of VTA putative DA in adolescent THC-pretreated rats relative to adolescent VEH-pretreated rats. Two-way repeated measures ANOVA or Two-tailed t-tests; **indicated p < 0.01. Error bars represent the standard error of the means (SEMs).