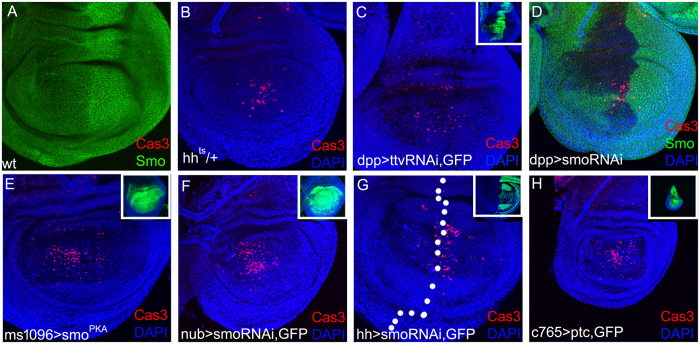
Figure 1.
Hh signalling activity is required for cell survival in Drosophila wing disc. In this and subsequent figures, wing discs are oriented with dorsal up and anterior left. (A) In the wild-type wing disc, there is no obvious apoptosis indicated by anti-Caspase-3 staining (red). The smo expression pattern is revealed by anti-Smo staining (green). (B) Heterozygote of a hh temperature-sensitive mutant allele showing the induction of apparent cell death (red). (C) Suppression of Hh transportation from posterior to anterior by expressing ttv-RNAi in the dpp-Gal4 domain (inset panel, green) results in apparent cell death (red). (D) Smo (green) is suppressed by expressing smo-RNAi in the dpp-Gal4 domain, and that induces massive cell death (red). (E) Suppressing smo by expressing a mutant smo PKA in all the wing pouch cells induces massive cell death (red). ms1096-Gal4 is expressed in all the wing pouch cells with a higher activity within the dorsal compartment (See inset panel, green). (F and G) Suppressing smo by expressing smo-RNAi in large regions induces massive cell death (red). The nub-Gal4 domain covers the pouch region (See inset panel in F, green). hh-Gal4 is expressed only within the posterior compartment (See inset panel in G, green). (H) Suppressing Smo activity by expressing the inhibitor gene ptc in all the wing cells under the c765-Gal4 driver results in small wing discs with massive cell death (red). Note that panel H is also from a 3rd instar larvae and is shown at the same magnification with other pannels. When ptc is expressed in the whole wing disc, the wing disc size is reduced apparently due to a proliferation defect.