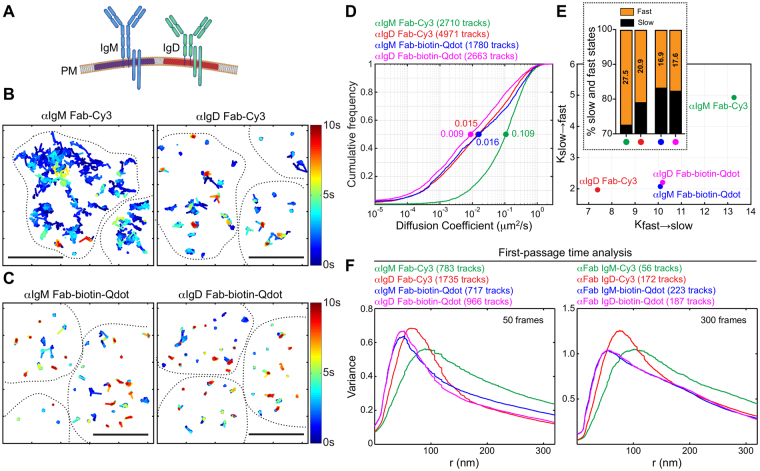
Figure 4.
Lateral diffusion of IgM-BCRs and IgD-BCRs cannot be distinguished using Qdot-labelling. (A) Schematic representation of IgM- and IgD-containing BCRs. (B–F) Ex vivo splenic B cells were labelled with anti-IgM or anti-IgD (αIgD) Fab-Cy3 probes (B) or with anti-IgM or anti-IgD Fab-biotin-Qdot probes (C). In panels B and C, trajectories are plotted using a colour-coded temporal scale. The dashed lines indicate cell boundaries. Scale bars = 5 μm. Cumulative frequency plots of single-state diffusion coefficients are shown (D). Median values are indicated by the dots. In panel (E), tracks were analyzed using the FPT algorithm. Histograms depicting the confinement radii for short tracks (50 frames, left panel) and long tracks (300 frames, right panel) are shown. In panel (F), the tracks were analyzed using the two-state HMM. The transition rates (Kslow→fast, Kfast→slow) between the two states are shown. The inset shows the fraction of time that receptors exhibited slow (red) versus fast (blue) diffusion, as determined using the two-state HMM. All data in panels (B–F) are from the same experiment. Similar results were obtained in two independent experiments.