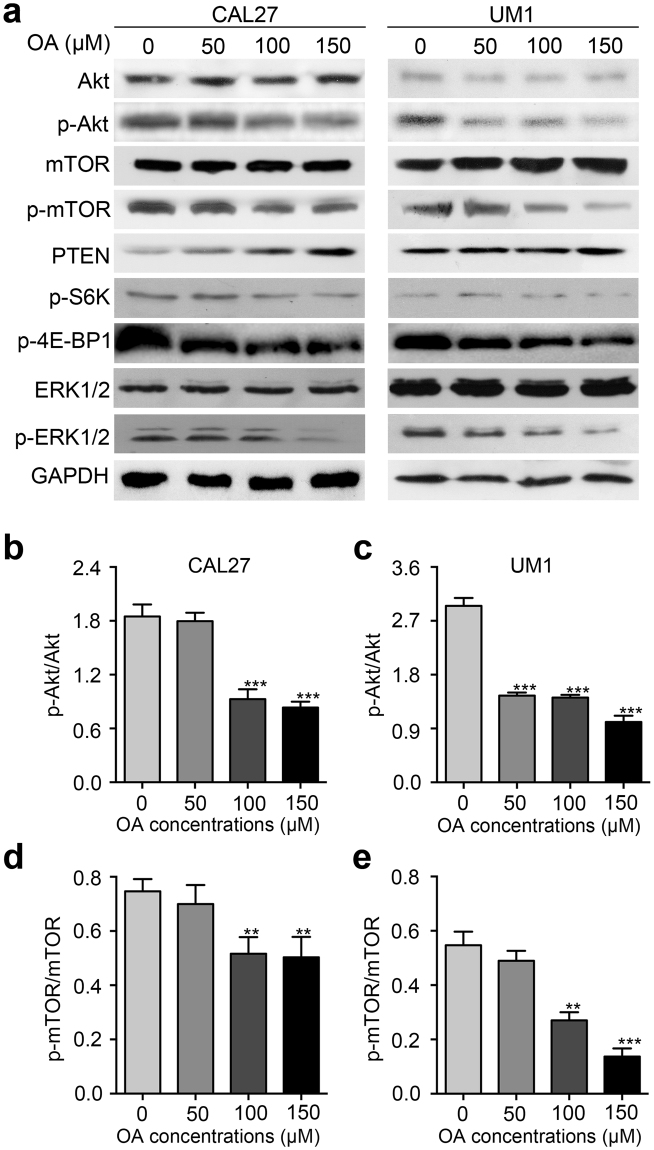
Figure 5.
OA inhibits the Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. (a) Western blot displaying the expression levels of Akt, p-Akt, mTOR, p-mTOR, PTEN, p-S6K, p-4E-BP1, p-ERK1/2, and ERK1/2 in CAL27 and UM1 cells after treatment with OA for 24 h. GAPDH was used as the internal control. (b–e) The protein expression levels from the above Western blot were quantitated. Bar graphs showed that the p-Akt/Akt ratio and p-mTOR/mTOR ratio were significantly decreased after treatment with OA. OA induced a decreased in p-Akt protein expression from 2.1-fold to 0.9-fold and from 3.2-fold to 1.2-fold in CAL27 and UM1 cells, respectively. p-mTOR expression was decreased from 0.78-fold to 0.59-fold in CAL27 cells and from 0.6-fold to 0.2-fold in UM1 cells. The results are presented as the mean ± standard deviation for three independent experiments (**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001).