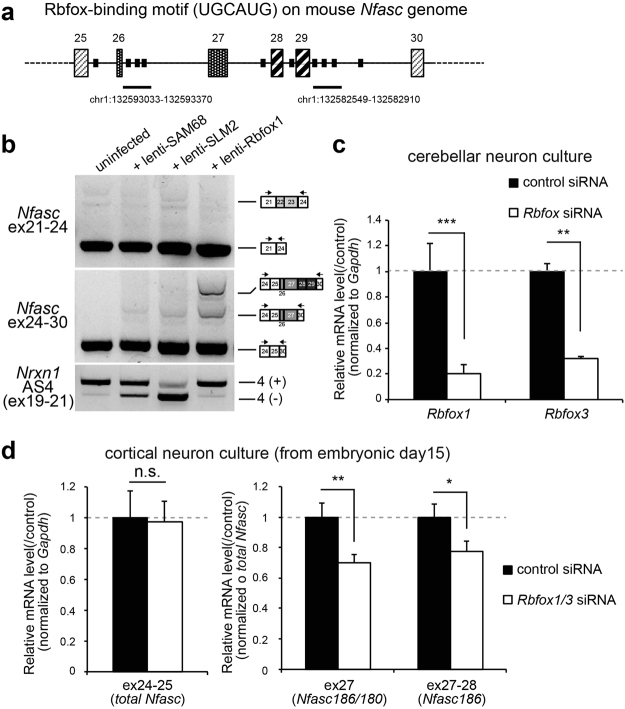
Figure 6.
The Rbfox family induces inclusion of ex26-29 in neuronal Nfasc. (a) Position of the Rbfox-binding element UGCAUG on the mouse Nfasc genomic sequence on chromosome 1 (qE4). Underlines show the intronic sequence, which had been isolated using a previously reported CLIP assay15. (b) Shift in alternative splicing at Nfasc ex26-29 in cerebellar GCs overexpressing Rbfox1. Neuronal splicing factors, SAM68, two SAM-like molecules, SLM1 and SLM2, and Rbfox1 were overexpressed in cerebellar GC cultures via lentiviral infection. Rbfox1 expression induced inclusion of Nfasc ex26-29 both selectively and markedly. In contrast, neither SAM68 nor SLMs had any effect on Nfasc splicing. Inclusion of exon20 at Nrxn1 at AS4 was accessed to confirm selective splicing activity of SAM68 and SLM proteins. (c) Rbfox1 and Rbfox3 knockdowns in cerebellar GC cultures by cell permeable siRNAs (1 μM, respectively). RT-qPCR confirmed that endogenous transcripts of Rbfox1 and Rbfox3 were reduced by approximately 80%. (n = 4 cultures). Values for the controls were set to 1.0. (d) Effect of double-knockdown by Rbfox1/3 siRNAs on splicing of Nfasc in cultured cortical neurons. A qRT-PCR study showed that double-knockdown of Rbfox1 and Rbfox3 significantly attenuated the inclusion of ex27-28 without affecting the total transcript level of Nfasc (ex24-25). (n = 4 cultures). Values for the controls were set to 1.0.