Figure 7.
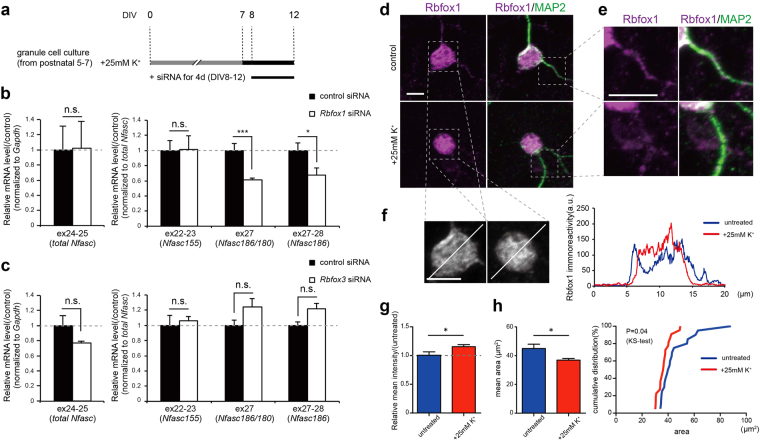
Rbfox1 selectively induces depolarization-dependent inclusion of ex26-29 in neuronal Nfasc. (a) Schematic diagram of the knockdown experiment by cell permeable Rbfox1 siRNA in a high K+-treated neuronal culture. Cerebellar GCs were maintained in high-K+ (30 mM) media from 7 DIV through 12 DIV to induce inclusion of ex26-29. Rbfox and control siRNAs were applied for the last 4 days before harvest. (b,c) Knockdown effect of Rbfox1 and Rbfox3 siRNAs on alternative splicing of Nfasc. (b) Knockdown of Rbfox1 significantly attenuated the high K+-induced inclusion of ex27-28 without affecting the total Nfasc transcript (ex24-25) levels. (c) In contrast, knockdown of Rbfox3 did not have an effect on the inclusion. (n = 4 cultures). Values for the controls were set to 1.0. (d–f) Representative images of subcellular localization of Rbfox1 protein in untreated and depolarized cerebellar GCs. (d) Cultures were stained with anti-Rbfox1 antibody 1D10. MAP2 was co-stained to visualize overall morphology of the cultured neurons. Scale bar = 5 µm. (e) High magnification images of dendritic processes. Scale bar = 5 µm. (f) High magnification images of cell somas and the line scans from untreated and depolarized cerebellar GCs displaying immunoreactivity for Rbfox1 on these cell somas. Scale bar = 5 µm. (g) Relative mean intensity of Rbfox1 immunoreactivity on cell somas in untreated and depolarized cerebellar GCs. (n > 20 neurons each group in two sister cultures). Values for untreated cultures were set to 1.0. (h) Rbfox1-localized area (left) and the cumulative probability distribution (right) on the cell somas in control and depolarized cerebellar GCs. (n > 20 neurons each group in two sister cultures).