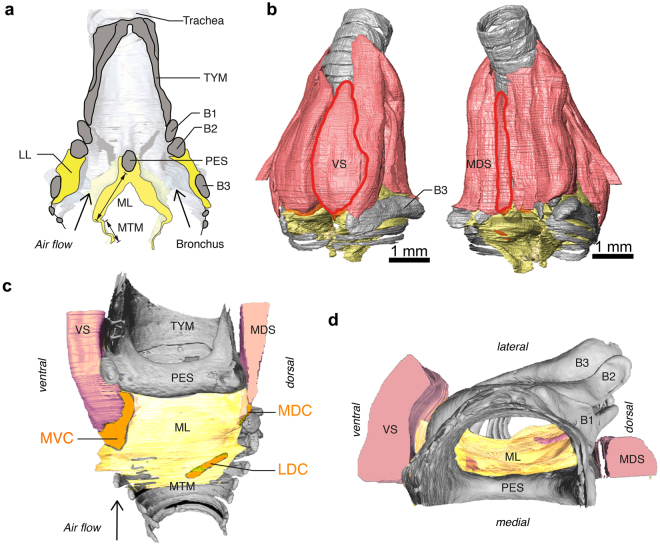
Figure 1.
Syrinx morphology. (A) Schematic sagittal cross-section through the syrinx showing the syringeal skeleton (grey) with the paired soft tissue masses LL and MVM (yellow). Muscles are omitted for clarity. (B–D) Micro-computed tomography scan of the zebra finch syrinx (modified from ref. 30) showing bones (grey), cartilaginous pads (orange), muscles (pink) and sound producing MVM (yellow). (B) Ventral and dorsal view with the two muscles (red outlines) that directly attach on cartilaginous pads embedded in the medial labium, VS and MDS. (C) Medial view on the MVM with only soft tissues of right bronchus visible and left bronchus removed for clarity. The tympanum is the bony cylinder that is formed of fused tracheal rings. The pessulus is an ossified medial dorso-ventral bridge of the tympanum dividing the two bronchi. (D) Top view of panel C. For a detailed description of the zebra finch syrinx including 3D interactive PDF figures see ref. 30. Abbreviations: B1-3, bronchial bones 1-3; LDC, latero-dorsal cartilage; LL, lateral labium; MDC, medio-dorsal cartilage; MDS, musculus syringealis dorsalis medialis; ML, medial labium; MVC, medio-ventral cartilage; MVM, medial vibratory mass; PES, pessulus; TYMP, tympanum; VS, musculus syringealis ventralis.