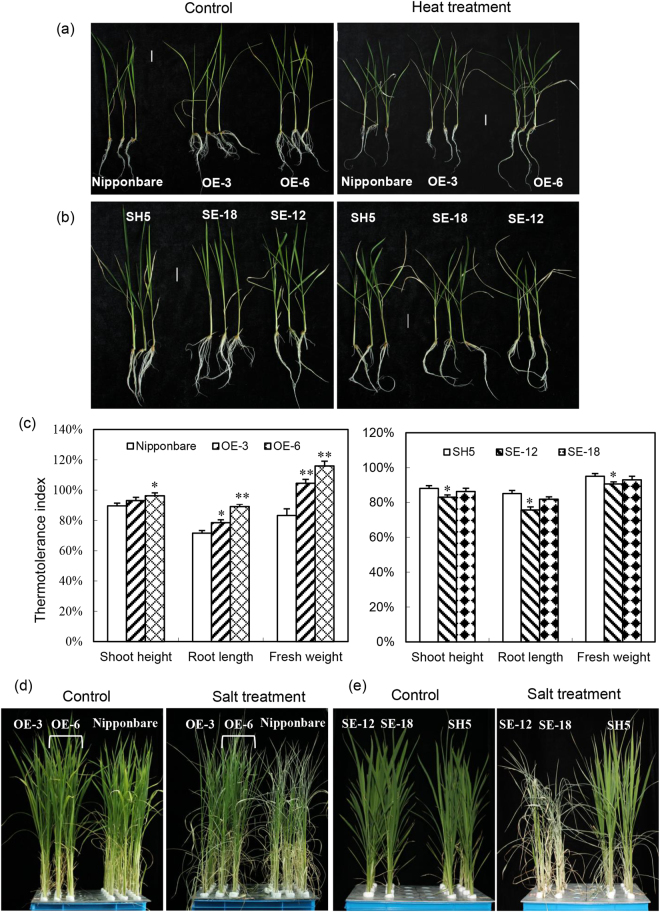
Figure 7.
The roles of OsHsp18.0 in thermo- and salt-tolerance. (a) OsHsp18.0-overexpressing lines OE-3 and OE-6 exhibited higher thermotolerance than wild-type Nipponbare. The 4-d seedlings of Nipponbare and transgenic lines were subjected to heat treatment. The representative plants were photographed after recovery at 28 °C for 14 d. Bars = 2 cm. (b) The thermotolerance of OsHsp18.0-silenced transgenic plants SE-18 and SE-12 was reduced compared with wild-type SH5 plants. (c) Comparisons of the thermotolerance indexes between transgenic and wild-type plants. The thermotolerance indexes were calculated as described in Materials and Methods. The asterisks indicate that a significant difference (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01) was detected between transgenic plants and the wild type. (d) OsHsp18.0-overexpressing transgenic lines OE-3 (column 1) and OE-6 (column 2–3) displayed enhanced tolerance to salt stress relative to the wild-type Nipponbare. (e) OsHsp18.0–silencing lines SE-18 and SE-12 were more sensitive to 200 mM NaCl than wild-type SH5. The photos in (d) and (e) were taken at 5 d post salt treatment.