Fig. 1.
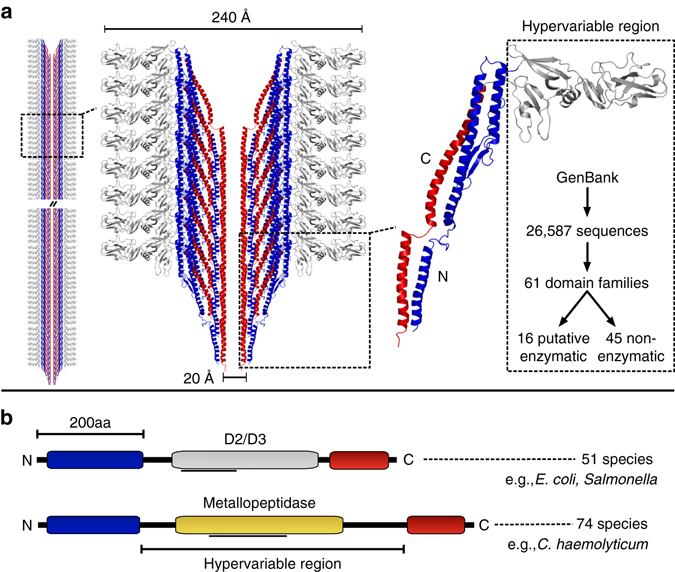
Structural model of the flagellar filament and identification of uncharacterized surface-exposed flagellin domains. a Structural model of the flagellar filament and constituent flagellin proteins (left), highlighting the interior flagellin N-terminal (blue) and C-terminal (red) domain and the surface-exposed hypervariable region domain (gray). The model is based on the structure of FliC from Salmonella (PDB 1ucu). Flagellin hypervariable regions from the NCBI GenBank database were analyzed, revealing 61 putative domain families including several with potential enzymatic function. b Schematic depiction of the commonly studied D2/D3 flagellin domain variant, as well as the novel putative metallopeptidase domain predicted within 74 species. The gray lines below the domains indicate regions matched by the Conserved Domain Database, which were manually refined through subsequent analysis
