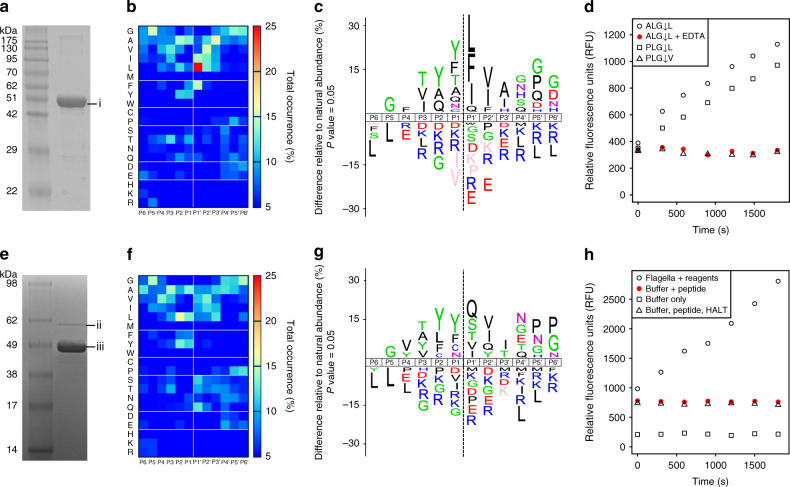
Fig. 4.
Peptidase activity assays of purified recombinant FliA(H)-hypervariable region and flagellar filaments from C. haemolyticum. a 12% SDS-PAGE of purified FliA(H)-hypervariable region (band “i”), electrophoresing close to that predicted for recombinant thioredoxin-tagged flagellin hypervariable region (50.14 kDa). b Amino acid occurrence heat map based on FliA(H)-hypervariable region protease cleaved peptide alignments of 391 cleavage sites identified in a tryptic E. coli K12 library. c IceLogos of FliA(H)-hypervariable region protease cleaved peptide specificity profiles showing percent differences compared to natural amino acid abundance, with significantly over-represented amino acids shown above the x-axis and under-represented residues below the x-axis. Amino acids that have not been identified are depicted in pink. d Fluorometric peptidase assays for FliA(H)-hypervariable region protease against three different peptidic substrates (ALG↓L, PLG↓L, PLG↓V) and + /– EDTA as indicated. e 10% SDS-PAGE of purified flagellar sheared filaments from C. haemolyticum. Band “ii” and “iii” were identified by mass spectrometry as FliA(H) (proteolytic flagellin) and the non-protease-containing structural flagellin (WP_039229459), respectively (Supplementary Fig. 7). f Amino acid occurrence heat map and g IceLogo based on cleaved peptide alignments of 269 cleavage sites identified in a tryptic E. coli K12 library using purified flagellar filaments. h Fluorometric peptidase assays for flagellar filaments using the ALG↓L peptide in three assay conditions including EDTA-free HALT protease inhibitors