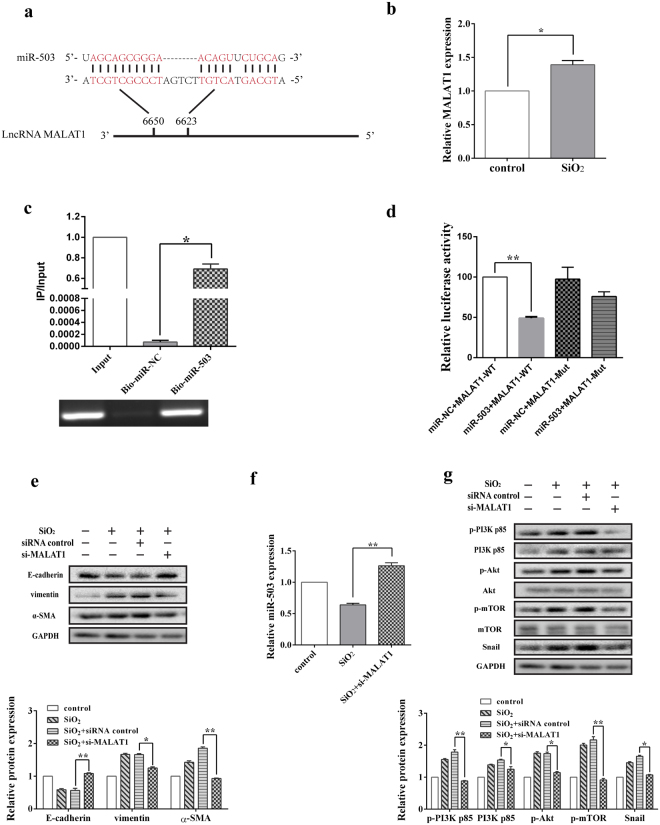
Figure 6.
LncRNA MALAT1 promotes EMT via binding to miR-503 directly. (a) Predicted binding sites for miR-503 in MALAT1. (b) The relative expression level of lncRNA MALAT1 was significantly increased in HBE cells after treated with 200 μg/ml silica for 48 h compared to the control group, *P < 0.05 versus the control group. (c) MALAT1 is associated with miR-503. Biotinylated miR-503 (bio-miR-503) and miR-NC were incubated with the extracted RNA of HBE cells (10 μl of the RNA samples were reserved for input) to pull down lncRNA MALAT1. After the biotin-labeled pull-down assay, MALAT1 expression levels were analyzed by qRT-PCR and RT-PCR, *P < 0.05 versus the Bio-miR-NC group. (d) The luciferase reporter gene assay was performed to identify the interaction between lncRNA MALAT1 and miR-503 in HBE cells. Luciferase activities were calculated as the ratio of firefly/renilla activities and normalized to the miR-NC + MALAT1 WT group, **P < 0.01 versus the miR-NC + MALAT1 WT group. (e) LncRNA MALAT1 siRNA was transfected to HBE cells and significantly alleviated the process of EMT assessed by Western blot, *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 versus the SiO2 + siRNA control group. (f) The level of miR-503 in HBE cells was increased after silencing of MALAT1 determined by qRT-PCR, **P < 0.01 versus the SiO2 group. (g) The protein levels of p-PI3K p85, PI3K p85, p-Akt, p-mTOR and Snail were repressed with the treatment of si-MALAT1, *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 versus the SiO2 + siRNA control group.