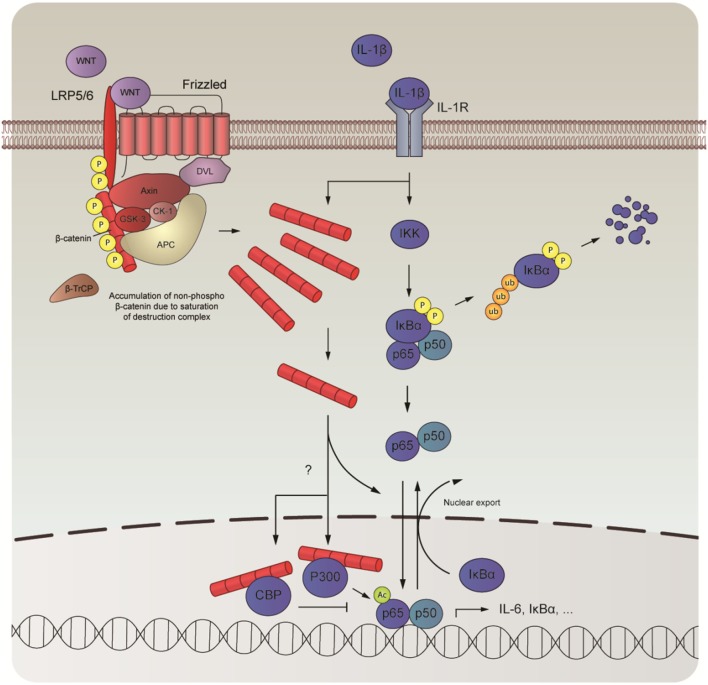
Figure 6.
Schematic overview of the interaction between nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and β-catenin. In human airway smooth muscle, interleukin-1β (IL-1β) drives the expression of proinflammatory genes, such as IL-6, by interacting with the WNT-effector β-catenin. Although IL-1β does not directly influence expression levels of β-catenin, it directs its nuclear import together with the NF-κB dimer to facilitate DNA-binding of p65. Inside the nucleus, β-catenin teams up with either CREB-binding protein (CBP) or P300, two mutually exclusive events that are necessary for transcriptional output by p65. While direct competition between CBP and P300 likely underlies binding with β-catenin, alternative mechanisms may also be at play. When bound, p65 is acetylated, which likely governs its subsequent transcriptional program.