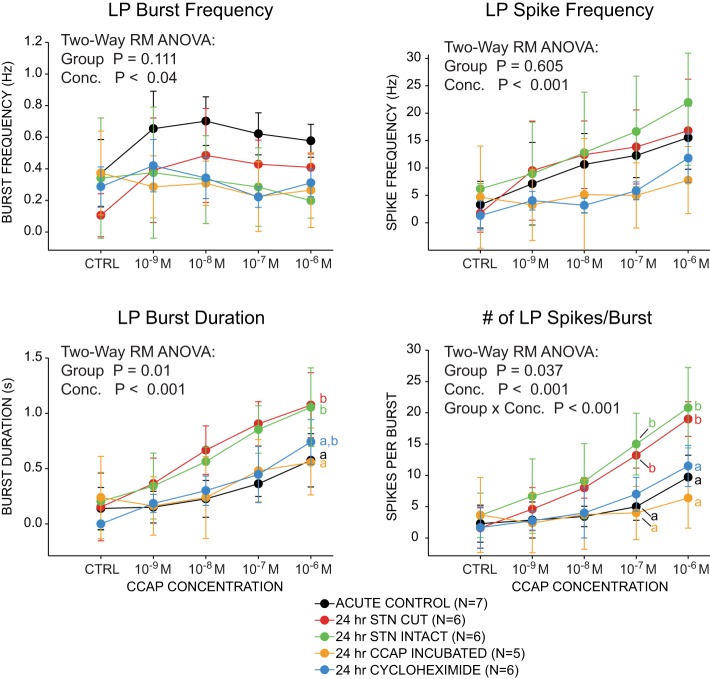
Fig. 3.
Changes in LP burst responses to CCAP application are due at least in part directly to loss of hormonal CCAP modulation. Data represented as means ± SD. There were significant differences in LP burst duration and number of spikes per burst across 5 different experimental manipulations. Results of 2-way repeated-measures ANOVAs are reported. Different superscripted letters indicate significant (P < 0.05) differences among groups as revealed by post hoc comparisons (i.e., groups labeled with different letters show significant differences from one another). Because no significant effect of group was detected for burst frequency and spike frequency, post hoc analyses were not performed. No interaction effect was found between group and concentration for burst duration, so we report results of post hoc analyses for the group factor only. Because a significant interaction effect was detected for spikes per burst, we report differences among groups at each concentration where the effect was found (i.e., 10−7 M and 10−6 M CCAP exposure). Sample sizes as indicated in key.