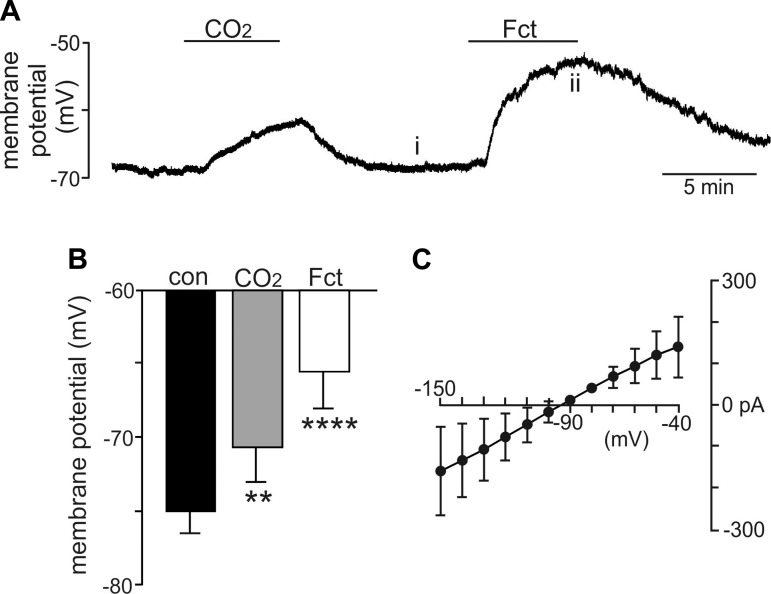
Fig. 1.
Bath application of fluorocitrate (FCt) results in a strong and reversible depolarization of chemosensitive astrocytes on the retrotrapezoid nucleus in vitro. A: trace of membrane potential from a chemosensitive retrotrapezoid nucleus (RTN) astrocyte shows that exposure to FCt (100 µM) caused a large depolarization. B: summary data (n = 6) show the membrane potential response to 15% CO2 and FCt. C: current-voltage (I-V) relationship of the FCt-sensitive difference current was determined at voltages between −150 and −40 mV by subtracting I-V relationships obtained under control conditions from those recorded during exposure to FCt. The FCt-sensitive current is fairly linear over this range of voltages and reverses at −95 mV, suggesting that FCt decreased conductance of 1 or more subthreshold K+ channels. Different from control (repeated-measures/1-way ANOVA; F2,5 = 28.004). **P = 0.02; ****P < 0.0001.