Figure 1.
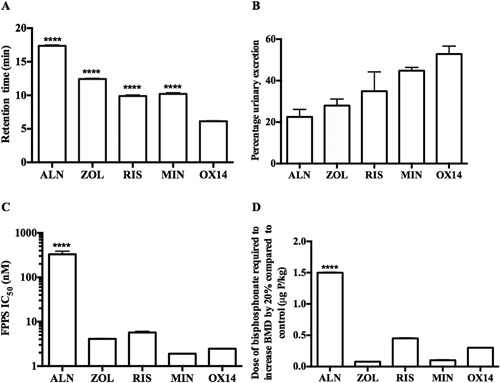
OX14 has a low bone‐binding affinity and is highly potent at inhibiting FPPS. (A) Retention of OX14 compared to other bisphosphonates on a HAP column over time. (B) Percentage urinary excretion of ALN, ZOL, RIS, MIN, and OX14 collected from 0 to 24 hours after i.v. injection. (C) FPPS inhibition assay of OX14 compared to other bisphosphonates. (D) The dose of ALN, ZOL, RIS, MIN, and OX14 (μg P/kg) that increased BMD greater than 20% compared to vehicle control in a growing rat model (proximal tibial metaphysis). Data are presented as mean ± SE (except 1B which is mean ± standard deviation) and significance compared with OX14 is indicated, where *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, and ****p < 0.0001.
