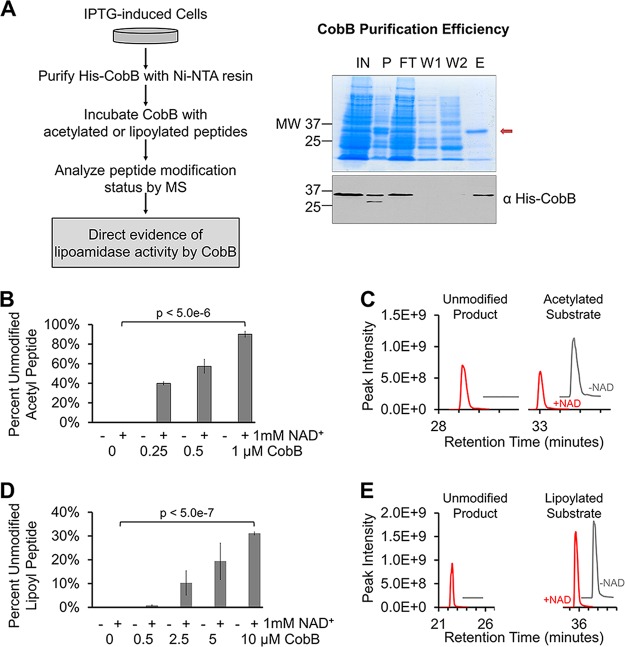
FIG 2 .
In vitro evidence for CobB lipoamidase activity. (A) Workflow developed to purify His-CobB and analyze enzymatic activity in vitro (left). Isolation of His-CobB, as shown on a protein gel (right, top) and Western blotting (right, bottom). His-CobB is indicated (red arrow) on the protein gel. His-CobB was seen on the Western blot when we used anti-His antibody. Lane labels: IN, input; P, pellet (insoluble fraction); FT, flowthrough; 1, wash 1; 2, wash 2; E, elution. (B) Percentage of unmodified peptide present after deacetylation of synthetic acetyl-peptide after 1-h incubations with various concentrations of CobB, with and without 1 mM NAD+ (n = 3). Synthetic posttranslationally modified H3K9 peptides were used in all in vitro assays. (C) Representative extracted ion chromatograms showing levels of resulting unmodified product (left) and remaining acetylated substrate (right) after 1-h incubation with 0.5 µM CobB. Chromatograms from reactions without NAD (-NAD) are offset for clarity (x axis, +2; y axis, +2e8). (D) Percentage of unmodified peptide present after removal of lipoylation from synthetic lipoyl-peptide after 1-h incubation with various concentrations of CobB, with and without 1 mM NAD+ (n = 3). (E) Representative extracted ion chromatograms showing unmodified product (left) and remaining lipoylated substrate (right) after 1 h with 10 µM CobB. Chromatograms from reactions without NAD are offset for clarity (x axis, +3; y axis, +2e8). Error bars represent standard deviations.