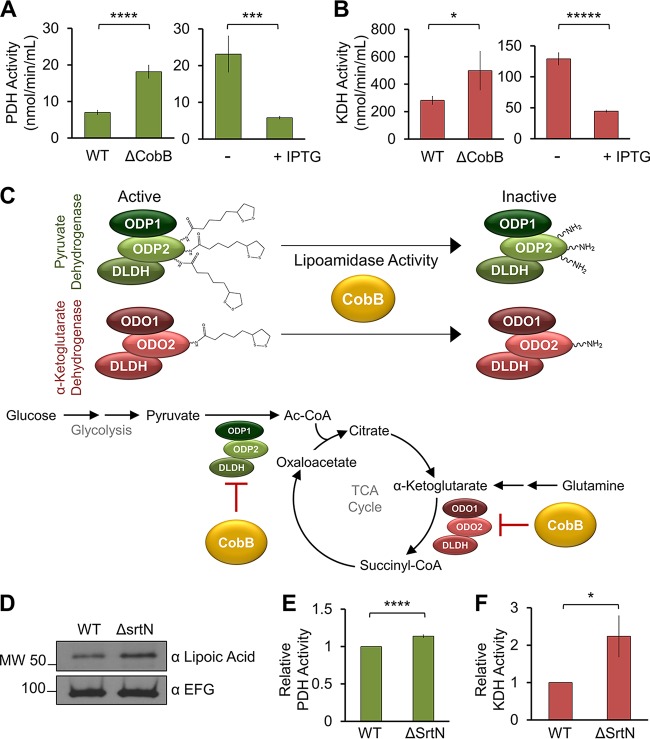
FIG 5 .
Sirtuins inhibit the activities of metabolic complexes in E. coli and B. subtilis. (A) Absolute PDH activity measured in WT and the ΔcobB deleetion mutant and in IPTG-treated and untreated cells (n = 3). ***, P < 0.005; ****, P < 0.001. (B) Absolute KDH activity measured as for panel A (n = 3), except for the ΔcobB strain (n = 2). *, P < 0.05; *****, P < 0.0005. (C, top) Proposed CobB-mediated lysine delipoylation reaction and resulting inhibition of complex activity. (Bottom) Proposed metabolic pathways under sirtuin regulation by lipoamidase activity. (D) Assessment of lipoyl levels via Western blotting with a ΔsrtN deletion mutant relative to WT B. subtilis. EFG was used as a loading control. (E) Relative PDH activity measured in WT and ΔsrtN mutant strain (n = 3). ****, P < 0.001. (F) Relative KDH activity as measured for panel (E (n = 3). *, P < 0.05. Error bars represent standard deviations.