FIG 4 .
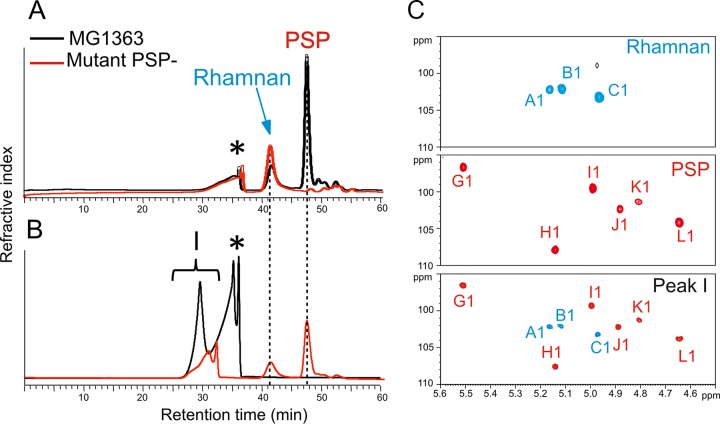
SEC-HPLC and NMR analyses of CWPS extracted from wild-type and PSP-negative mutant (VES5748) L. lactis MG1363. (A) SEC-HPLC separation of CWPS extracted by HF from MG1363 showing two polysaccharide signals identified as rhamnan and PSP-derived oligosaccharides, whereas VES5348 shows only rhamnan. (B) SEC-HPLC separation of cell wall products from MG1363 digested with mutanolysin showing a major polysaccharide signal (peak I in black). When hydrolyzed with HF, purified peak I regenerated rhamnan and PSP-derived oligosaccharides (red line). (C) Comparison of the anomeric regions of the 1H-13C HSQC NMR spectra of different compounds confirming that peak I contained both rhamnan and PSP-derived oligosaccharides. The attribution of PSP monosaccharide signals was based on previous NMR identification of intact and HF-generated oligosaccharides from the PSP (11, 14). Asterisks indicate nonpolysaccharide compound.