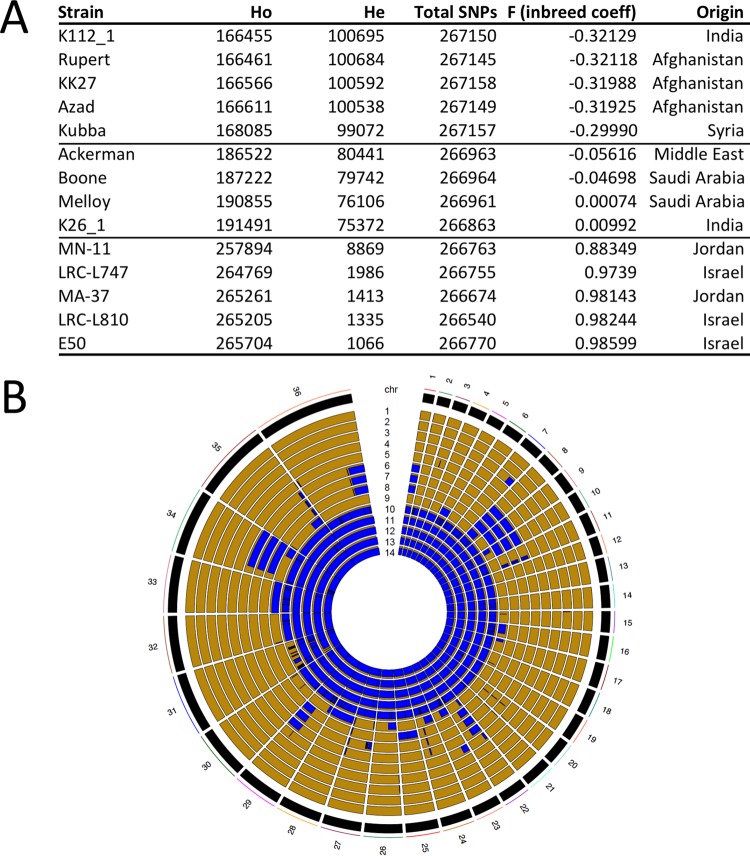
FIG 1 .
Heterozygosity and homozygosity among a total of 268,518 polymorphic sites identified by analyzing the genomes of 14 isolates of L. tropica. (A) Heterozygosity and homozygosity among the total 268,518 polymorphic positions in 14 isolates of L. tropica. The F statistic (inbreeding coefficient) and the number of heterozygous (He) and homozygous (Ho) positions were calculated using VCFtools. The isolates were sorted into low, intermediate, and high homozygosity groups, depending on the Ho. (B) LROH in 14 clinical isolates of L. tropica. The RCircos plot shows LROH for each of the 36 chromosomes, with homozygosity in blue and heterozygosity in gold. Note that no two isolates had the same exact pattern of LROH, despite many similarities among individual geographic groups (several isolates from Israel and Jordan were mostly homozygous, whereas the majority of the other isolates were largely heterozygous). The isolates represented in each panel are ordered in concentric rings, according to the F value (inbreeding coefficient) from panel A and numbered from 1 to 14, respectively: 1, K112_1 (India); 2, Rupert, Afghanistan; 3, KK27 (Afghanistan); 4, Azad, Afghanistan; 5, Kubba (Syria); 6, Ackerman (Israel); 7, Boone, Saudi Arabia; 8, Melloy (Saudi Arabia); 9, K26_1 (India); 10, MN-11 (Jordan); 11, L747 (Israel); 12, MA-37 (Jordan); 13, L810 (Israel); 14, E50 (Israel).