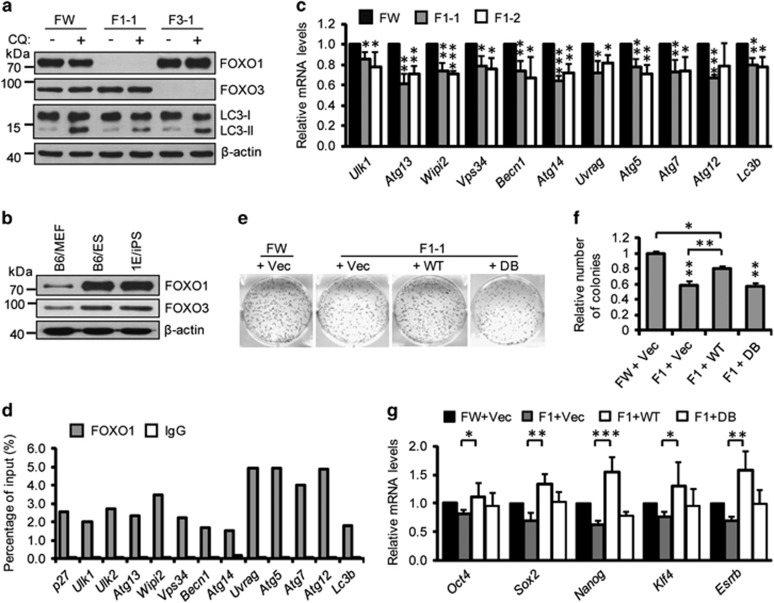
Figure 4.
FOXO1 drives an autophagy machinery gene program to maintain high autophagic flux. (a) Western blotting for LC3 in Foxo1 and Foxo3 knockout (KO) ESC lines. β-Actin served as the loading control. (b) Western blotting for FOXO1 and FOXO3 in B6/MEF, B6/ES, and 1E/iPS cells. β-Actin served as the loading control. (c) qPCR for autophagy-related genes in Foxo1 KO ESC lines. Data shown are mean±S.D., n=3, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 (Student’s t-test). (d) ChIP analysis of FOXO1 in B6/ES cells treated with rapamycin (200 nM) for 2 h. DNA co-immunoprecipitated with either anti-FOXO1 or a control pre-immune immunoglobulin (IgG) were quantitated by qPCR and normalized to input. Representative results from three independent experiments are shown. (e) Reacquisition of wild-type but not mutant Foxo1 expression in Foxo1−/− cells compensated for reprogramming efficiency. (f) Quantification of AP-positive colonies from (e). Data shown are mean±S.D., n=3, *P<0.05, **P<0.01 (Student’s t-test). (g) qPCR for pluripotency marker genes. Data shown are mean±S.D., n=3, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 (Student’s t-test). Images in (a and b) are representative of three independent experiments respectively