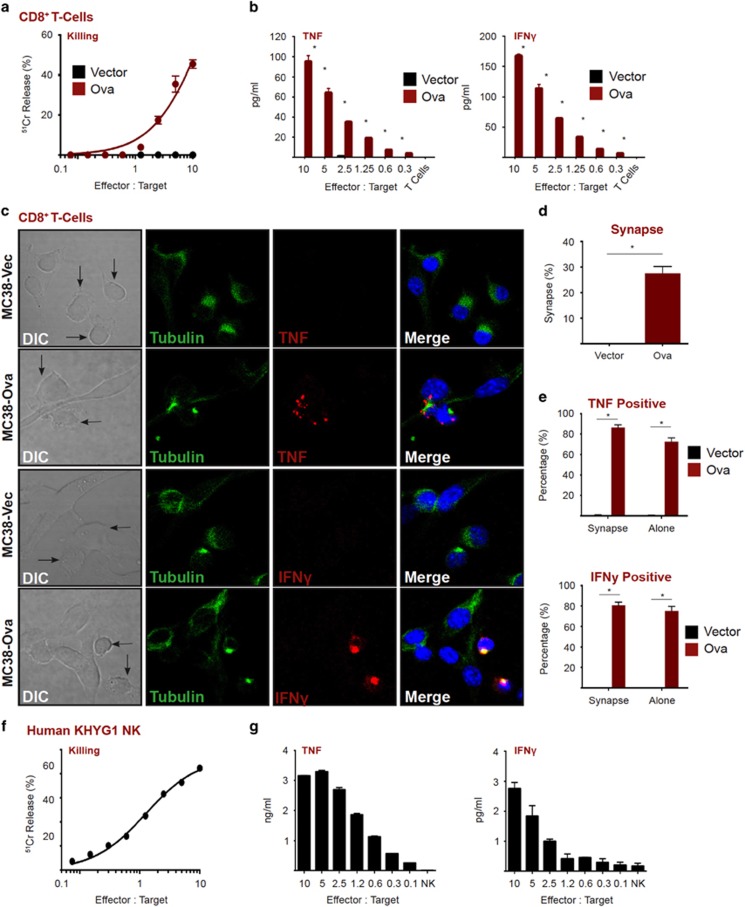
Figure 1.
Cytotoxic lymphocytes produce inflammatory cytokines upon tumor cell recognition. (a) Chromium release assay (4 h) using MC38-Ova cells as targets and OT-I T cells as effectors. (b) MC38-Ova cells were exposed to OT-I T cells at the indicated effector to target (E:T) ratio. After 5 h, cytokines in supernatants were measured by CBA. (c) MC38-Ova or vector cells were seeded in chamber slides then overlaid with OT-I T cells. After 2 h, cells were fixed, stained as indicated, then visualized by confocal microscopy. (d) The percentage of T cells that were in a synapse with a target cell was quantitated by confocal microscopy. (e) The percentage of T cells that were positive for the indicated cytokines was quantitated by confocal microscopy. A minimum of 100 cells was counted in each condition. (f) Chromium release assay (4 h) using HeLa cells as targets and KHYG1 NK cells as effectors. (g) HeLa cells were exposed to KHYG1 NK cells at the indicated effector to target (E:T) ratio. After 5 h, cytokines in supernatants were measured by CBA. Error bars represent the mean±S.E.M. of triplicate determinations from a representative experiment, *P<0.05 by unpaired Student’s t-test