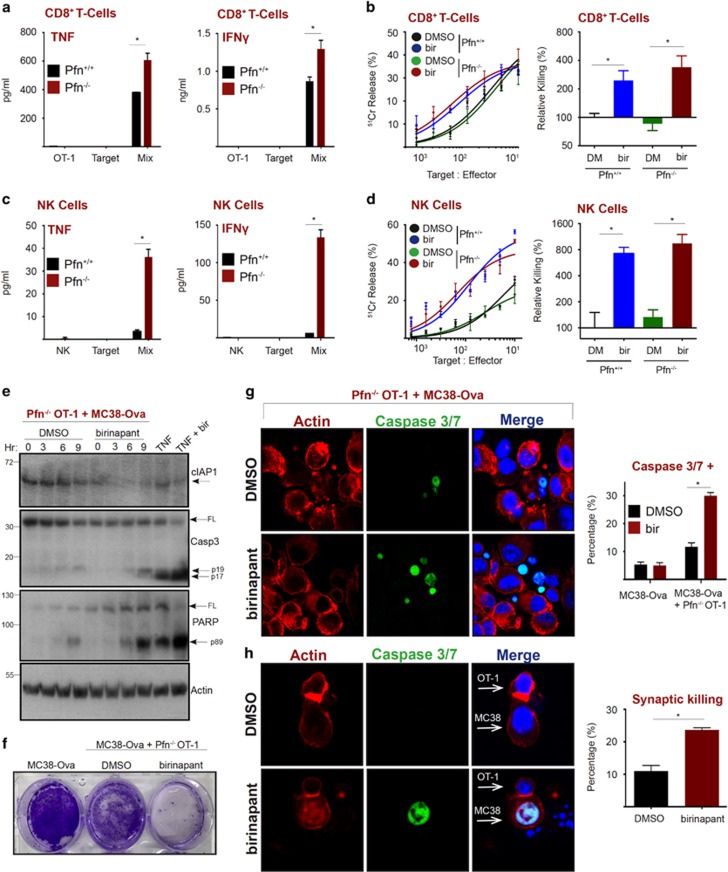
Figure 3.
IAP antagonism promotes perforin-independent CL killing. (a) MC38-Ova cells were exposed to Pfn+/+ or Pfn−/− OT-I T cells. After 5 h, cytokines in supernatants were measured by CBA. (b) Chromium release assay (18 h) using MC38-Ova cells as targets and Pfn+/+ or Pfn−/− OT-I T cells, in the presence or absence of birinapant (1 μM). (c) MC38-Ova cells were exposed to Pfn+/+ or Pfn−/− murine NK cells. After 5 h, cytokines in supernatants were measured by CBA. (d) Chromium release assay (18 h) using MC38 cells as targets and Pfn+/+ or Pfn−/− murine NK cells, in the presence or absence of birinapant (1 μM). (e) MC38-Ova cells (2 × 106) were exposed to 2 × 105 Pfn−/− OT-I T cells in the presence or absence of birinapant (1 μM). TNF (50 ng/ml) and birinapant (1 μM) were used as positive controls. At the indicated time-points, proteins were analyzed by western blotting. (f) MC38-ova cells (1 × 106) were exposed to Pfn−/− OT-I T cells (2 × 105). After 48 h, cells were visualized by crystal violet staining. (g–h) MC38-Ova cells were seeded in chamber slides then overlaid with Pfn−/− OT-I T cells. After 8 h, cells were fixed, stained as indicated, then visualized by confocal microscopy. A minimum of 50 cells was counted in each condition. Error bars represent the mean±S.E.M. of triplicate determinations from a representative experiment, *P<0.05 by unpaired Student’s t test